Bertil Blok, MD, PhD
- Department of Urology
- Erasmus Medical Center Rotterdam, Netherlands
Tolterodine dosages: 4 mg, 2 mg, 1 mg
Tolterodine packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
1 mg tolterodine order
Relation of physique composition, fats mass, and serum lipids to osteoporotic fractures and bone mineral density in Chinese men and women. Minireview: the stem cell next door: skeletal and hematopoietic stem cell "niches" in bone. Circulating osteogenic cells: characterization and relationship to rates of bone loss in postmenopausal girls. Glucose uptake and Runx2 synergize to orchestrate osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Strain-specific results of rosiglitazone on bone mass, physique composition, and serum insulin-like progress factor-I. Rosiglitazone induces decreases in bone mass and energy that are paying homage to aged bone. Hdac3 deficiency will increase marrow adiposity and induces lipid storage and glucocorticoid metabolism in osteochondroprogenitor cells. Regulation of stemness and stem cell area of interest of mesenchymal stem cells: implications in tumorigenesis and metastasis. Lactic acid manufacturing in mouse calvaria in vitro with and with out parathyroid hormone stimulation: lack of acetazolamide results. Bioenergetics throughout calvarial osteoblast differentiation reflect strain variations in bone mass. Bone marrow adipose tissue is an endocrine organ that contributes to increased circulating adiponectin during caloric restriction. Adiponectin regulates bone mass by way of reverse central and peripheral mechanisms through foxo1. Continuous therapy with a low-dose -agonist reduces bone mass by increasing bone resorption with out suppressing bone formation. Prevalence and predictive components for regional osteopenia in ladies with anorexia nervosa. Bone turnover during inpatient dietary therapy and outpatient follow-up in sufferers with anorexia nervosa in contrast with that in wholesome management topics. A 2-year prospective research of bone metabolism and bone mineral density in adolescents with anorexia nervosa. Inhibition of Pref-1 (preadipocyte issue 1) by oestradiol in adolescent ladies with anorexia nervosa is related to enchancment in lumbar bone mineral density. The effects of estrogen administration on bone mineral density in adolescents with anorexia nervosa. Alterations in cortisol secretory dynamics in adolescent ladies with anorexia nervosa and results on bone metabolism. Alterations in progress hormone secretory dynamics in adolescent women with anorexia nervosa and results on bone metabolism. Relation between features of dietary disturbance and menstrual exercise in main anorexia nervosa. Low leptin ranges predict amenorrhea in underweight and eating disordered females. Serum adiponectin and resistin concentrations in sufferers with restrictive and binge/ purge form of anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa. Relationships between serum adipokines, insulin ranges, and bone density in girls with anorexia nervosa. Anorexia nervosa is characterized by increased adiponectin plasma levels and lowered nonoxidative glucose metabolism. Neuropeptide Y and sex hormone interactions in humoral and neuronal regulation of bone and fat. Ghrelin and bone metabolism in adolescent women with anorexia nervosa and wholesome adolescents. Secretory dynamics of leptin in adolescent girls with anorexia nervosa and healthy adolescents.
Vitamin B17 (Apricot Kernel). Tolterodine.
- Are there safety concerns?
- How does Apricot Kernel work?
- Cancer. Apricot kernel and the active chemical amygdaline or Laetrile is not effective for treating cancer.
- What is Apricot Kernel?
- Dosing considerations for Apricot Kernel.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=97133
Generic 4 mg tolterodine with mastercard
Consequently, pathologic processes may alter normal venous circulate patterns and result within the transport of fabric into the mind. Posterior cerebral artery Vein of Galen malformation Bulging fontanelles, progressive hydrocephalus (resulting from occlusion of the cerebral aqueduct), and dilated veins in the face and scalp are attribute findings. Brainstem and Cerebellum the brainstem is drained by a loosely organized network of venous channels positioned on its surface. In common, these vessels enter bigger veins or venous sinuses positioned in the immediate vicinity. For example, veins of the midbrain enter the good cerebral and basal veins, whereas those of the pons and medulla could enter the petrosal sinuses and the cerebellar veins. The superior cerebellar veins enter the straight, transverse, or superior petrosal sinuses. The inferior cerebellar surface is drained by inferior cerebellar veins, which enter the inferior petrosal, transverse, or straight sinuses. For instance, a tumor or an infection in the orbit may trigger venous blood to flow toward the cavernous sinus somewhat than away from it. In this manner, infectious materials or tumor cells may move from the orbit into the cavernous sinus and, via its connecting channels, to other components of the mind. In these cases, the nice cerebral vein is grossly enlarged and fed by massive and abnormal branches of the cerebral and cerebellar arteries. The veins concerned are usually the bigger ones, such as the superficial veins on the cerebral cortex or the interior cerebral veins. On the other hand, cerebral venous thrombosis might happen after brain surgery, meningitis, sinus infections, traumatic head accidents, or gunshot damage to the head, especially those that may involve the sinuses. The occlusion of a venous construction reduces or blocks venous return and ends in a cascade of occasions. Upstream to the blockage, the veins and sinuses are engorged (venous stasis), the encompassing white matter becomes edematous, hemorrhage from the elevated venous pressure is feasible, and there are indicators and signs of increased intracranial strain (headache, nausea, vomiting, lethargy). The infarct created is known as a venous infarct because of its origin from venous constructions. The deficits experienced by the affected person could replicate the overall location of the venous thrombosis. For instance, thrombosis of the middle portions of the superior sagittal sinus might lead to elevated tone and weak spot of the opposite lower extremity or both decrease extremities due to the proximity of the occluded sinus to the motor cortex. Thrombosis of the caudal parts of the superior sagittal sinus could end in visual deficits due to venous stasis of the superior sagittal sinus. The terminal branches of the medullary arteries contribute to the formation of the arterial vasocorona. At about levels T10 to , L1, or L2, one spinal medullary (or probably a radicular) artery, normally on the left, is very giant. As in the case of the cerebral and cerebellar arteries, the spinal twine has watershed zones and may be vulnerable to watershed infarcts, particularly in midthoracic levels. Due to its diameter, even a small watershed infarct in the twine could lead to severe deficits. The anterior spinal artery provides off central (or sulcal) branches, which pass alternately to the right and to the left to serve central areas of the spinal twine. The posterior spinal arteries course on the surface of the spinal wire medial to the posterior root entry zone. The blood supply to the spinal twine is supplemented at most spinal ranges by branches of segmental arteries. Because the radicular arteries provide the posterior and anterior roots, every spinal degree has these branches. However, the spinal medullary arteries serve to complement the In common, the venous drainage of the spinal twine mirrors its arterial supply. There is intensive communication between spinal veins and the internal and external venous plexuses discovered adjacent to the dural sac and vertebral our bodies. The veins forming these plexuses apparently lack valves, and the circulate in these channels is easily reversed.
Purchase tolterodine 4 mg without prescription
The longitudinal progress price determines the age and amount of trabecular tissue within the metaphyseal zones of different bones. A faster longitudinal growth price leads to an increased amount of cancellous bone of a lesser age. In distinction, major bone tumors arising from the opposite main mesenchymal cell types. Relative to an age-matched vehicle-treated control (A), the handled animal (B) has markedly longer primary spongiosa. Chordomas are unusual axial skeleton neoplasms that arise from residual foci of primitive notochord anywhere along the ventral areas of the vertebral column, but they most commonly involve the cranial (skull) and caudal (tail) portions. They are slow-growing however highly infiltrative masses, producing bony destruction and incessantly extending into adjoining gentle tissues. They have been reported as spontaneous lesions in people, rats, mice, canines, ferrets, and mink. Bone Modeling Alterations Bone modeling as a process happens principally during growth, but continues to a small extent all through life. Toxic responses that depend upon altered bone modeling have an result on compact bone and lead to insufficient or extra accumulations of bone or to mechanically inappropriate architecture. Reactivation of bone modeling can happen in adult animals, as in the formation of marginal osteophytes in affiliation with joint instability and degenerative arthropathy. Relative to a management animal (left), the rib from a rat given a bisphosphonate (right) reveals intensive filling of the medullary cavity with retained main spongiosa with outstanding cartilage cores. Osteoclast-mediated bone resorption could happen because T-lymphocytes secrete interleukin-1 (formerly generally recognized as osteoclastactivating factor). Bone Turnover Alterations Bone turnover is an ongoing process underneath the influence of many alternative factors, both systemic and local. In the growing bone, as soon as the primary spongiosa is shaped, the number of trabeculae is decreased by osteoclasts and their thickness increased by osteoblasts. The scalloped cartilage cores and reversal cement strains inside metaphyseal trabeculae are evidence of this activity. If osteoclastic resorption of the metaphyseal trabeculae is inhibited, elevated bone results (such as after bisphosphonate administration). The amount of metaphyseal bone additionally could additionally be elevated if the biomechanical load is enhanced or anabolic brokers are administered. Any factor, including drugs and toxicants, that increase the rate of bone turnover within the metaphysis will lead to decreased bone. This finding will develop quickly as reduced numbers and thickness of bony trabeculae since there usually is a loss within the amount of cancellous bone throughout metaphyseal turnover. In contrast, osteopenia refers to the state in which total bone mass is reduced, but remaining bone is qualitatively regular. With growing older, the amount of bone removed throughout remodeling declines, but the quantity of bone that refills the resorption pit. Any condition or drug that enhances this deficit may cause irreversible bone loss, together with malnutrition, excessive endogeneous levels or exogenous doses of corticosteroids, and chronic metabolic acidosis (which causes preferentially cortical bone loss in rats). Osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and fibroblasts may be recognized in the lesion, as can fibrous tissue, osteoid, and woven bone. Dietary estrogens have been proven to hasten the event of increased bone and are thought of to be one of the many factors predisposing C3H mice to the development of osteosarcoma. Previous trauma or infection can lead to focal areas of decreased or elevated bone. Metastatic neoplasms of soft tissues that spread to bone trigger focal bone loss that may be detected radiologically. Such metastases might happen by direct invasion, however normally observe hematogenous unfold and seeding of the bone marrow. Common Toxicant-Induced Responses in Joints Toxicant-related responses in joints following exposure to exogenous chemical substances or biologics could affect any of the many intraarticular tissues. With acute exudative reactions, edema and fibrin deposition in the joint may be considerable, with solely a restricted inflammatory cell infiltrate.
Buy 2 mg tolterodine otc
However, there may be situations when this may not be applicable, similar to discussing a selected prognosis that has a well-established therapy strategy. A patient could also be referred to the genetics skilled with a prognosis that wants to be confirmed, or the patient may be referred to a scientific geneticist to make a genetic diagnosis. Regardless of the setting, the elements of the genetic counseling session are similar. This permits the genetics supplier to dispel any initial misconceptions relating to the aim and potential outcomes of the genetic counseling session together with genetic testing. The "pedigree process" additionally allows one to appropriate any misapprehensions the affected person might have about the diploma of heritability in a household for any given diagnosis. Families might have long-held beliefs concerning the causes of certain issues within the family. For instance, relations may falsely attribute start trauma as the cause for a disorder, or imagine that a certain dysfunction impacts only males since the entire females in their family are unaffected. The responsibility to warn relatives with respect to their genetic threat is an ethical problem that always must be addressed during this portion of the genetic counseling session. This duty might convey up a mess of concerns, including patient confidentiality and the autonomy of relatives in having the power to choose not to know of their danger standing. While the focus of the counseling session ought to remain on the affected person and the family members current, genetic counseling must include steering as to why and the means to talk about the prognosis and potential impact with other family members, and to guide them to appropriate resources. As such, sufferers have to be counseled as to the actual and potential risks, advantages, and alternate options to testing, and likewise be given the help needed to make an informed choice relating to their testing options. It is worth noting that patients may very well put more weight on their perceived risk and 1. Pretest genetic counseling additionally permits for a dialogue of the potential for unclear or unexpected findings, similar to variants of unknown significance, incidental/ secondary findings, and nonpaternity. Genetic testing in the setting of childhood and adolescence is an issue that continues to be debated within the genetics field. Multiple skilled societies have taken the stance that testing of minors ought to solely be accomplished when the disorder in question has a childhood onset and effective therapy or surveillance in childhood is available. The potential advantages, corresponding to elimination or discount of uncertainty, or the initiation or elimination of surveillance methods, must be weighed against the potential harms, similar to elevated anxiousness or results on familial relationships. Another concern that has been highlighted with regard to genetic testing is the "responsibility to recontact. Patients can also must be recontacted within the setting of beforehand recognized variant of unknown significance being reclassified as a causal or "normal" variant. Does a genetics clinic have the suitable infrastructure and resources required to recontact all relevant sufferers with new testing choices How will the first care provider keep current information on the event of recent genetic checks Genetic testing poses unique challenges because the disclosure of genetic information, whether or not voluntary or involuntary, has the potential to lead to social and economical consequences. Genetics providers function beneath the assumption of full disclosure; households must be given all related data as it pertains to the prognosis. In addition, it is most likely not appropriate or possible to disclose every piece of information relating to a dysfunction, genetic take a look at, or therapy as the provision of an extreme amount of info during a single session may result in confusion and negatively 1. For instance, when providing prenatal genetic counseling to a pair who already have a toddler with a skeletal dysplasia, an in depth rationalization of prenatal testing choices may be more acceptable than a prolonged discussion of the prognosis of the dysfunction. Alternatively, in the pediatric setting, an extensive description of prenatal diagnostic testing will not be acceptable when the family is primarily interested in confirming the prognosis and acquiring prognostic data for his or her baby. Indeed, genetic counseling aims to present patients with the information they might want to make the most informed and autonomous determination potential at that time. In genetic counseling practice, as the time period "danger" may be seen as a adverse time period, the phrases "likelihood" or "chance" are sometimes most popular. The ability of a affected person to recall the quantitative danger figure they got may not provide perception into how they understand that danger, nor the steps they might take to mitigate the danger. Thus, genetic counseling ought to concentrate on understanding how the chance is internalized by the affected person rather than the regurgitation of the risk figure. Therefore, dangers must be offered utilizing a wide selection of strategies, together with fractions, percentages, and scales. Following the chance dissemination, sufferers must be asked questions, similar to "Is this a quantity you anticipated
Best 1 mg tolterodine
However, sure so-called lengthy loop reflexes transmit muscle sensory info via ascending pathways that attain the cerebral cortex by means of a thalamic relay. The cortex can then improve or lower the achieve of spinal reflexes through descending supraspinal pathways. Of the several pathways that project to the spinal cord from the brainstem or cerebral cortex, four are particularly relevant to voluntary movement. Two of them, the vestibulospinal and reticulospinal methods, travel within the ventral funiculus of the spinal cord. The other two, the rubrospinal and lateral corticospinal tracts, journey in the lateral funiculus. The following sections focus on the three techniques that originate in the brainstem: the vestibulospinal, reticulospinal, and rubrospinal tracts. The medial vestibulospinal tract is made up of axons that originate within the medial and inferior vestibular nuclei and descend bilaterally into the spinal cord as part of the medial longitudinal fasciculus. The medial vestibulospinal tract projects solely so far as cervical or higher thoracic spinal twine levels and influences motor neurons controlling neck musculature. The lateral vestibulospinal tract, in distinction, extends all through the size of the twine. Cells in rostral parts of the lateral vestibular nucleus project to the cervical wire, cells within the middle portion project to the thoracic cord, and cells in the caudal part terminate in lumbosacral levels. These muscle tissue perform to counteract the force of gravity and subsequently are generally called antigravity muscles. Through their results on these extensor muscular tissues, lateral vestibulospinal fibers function within the management of posture and stability and, therefore, are also sometimes specified as postural muscular tissues. Evidence from experimental research means that some vestibulospinal axons synapse directly on alpha motor neurons, however most exert their influence through spinal interneurons. The two sources of excitatory input are the vestibular sensory apparatus and the cerebellar nuclei, mainly the fastigial nucleus. The lateral vestibulospinal tract is the path by which enter from the vestibular sensory equipment is used to coordinate orientation of the head and body in space. Maintenance of body and limb posture is also influenced by in depth cerebellovestibular projections, which could be both excitatory or inhibitory. Reticulospinal fibers take part in a extensive variety of functions ranging from ache modulation to visceromotor activity. The fibers from the oral and caudal pontine reticular nuclei descend bilaterally, however with an ipsilateral predominance, within the anterior funiculus. They represent the medial reticulospinal (or pontine reticulospinal) tract, which runs the full size of the spinal twine. The fibers from the gigantocellular reticular nucleus originate at medullary ranges. The reticulospinal system is activated by ipsilateral descending cortical projections (corticoreticular fibers) as nicely as by ascending somatosensory techniques (spinoreticular fibers), mainly those conveying nociceptive signals traveling within the anterolateral system. Through its affect on gamma motor neurons, the reticulospinal system is involved in the upkeep of posture and in the modulation of muscle tone. Pontine reticulospinal fibers tend to mediate excitatory effects, and medullary reticulospinal fibers usually produce inhibitory effects. These fibers descend by way of the brainstem contralateral to their origin and enter the spinal twine anteriorly adjoining to the lateral corticospinal tract. In mammals which were investigated and doubtless additionally in humans, the magnocellular half provides rise to most rubrospinal fibers, and the parvocellular half gives rise to rubroolivary fibers. In general, the rubrospinal fibers descend to the contralateral spinal cord and the rubroolivary fibers to the ipsilateral inferior olivary nuclei. The magnocellular portion of the red nucleus is comparatively smaller in humans than in different mammals, and the rubrospinal tract is correspondingly small. In addition, relatively few rubrospinal axons seem to prolong caudal to the cervical enlargement in people, suggesting that this technique is primarily concerned with the higher extremity. Clinical findings in sufferers are consistent with this conclusion, indicating that the rubrospinal system exerts its control mainly over the upper extremity and has little, or no, influence over the lower extremity.
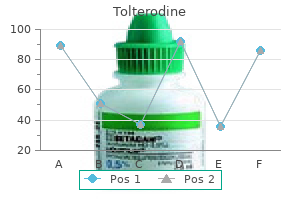
Purchase 1 mg tolterodine with mastercard
Rather, these cells are scattered inside nerve plexuses of the target organ or in the wall of the gut (terminal or intramural ganglia), where they intermingle with neurons of the enteric nervous system. The visceral motor element of the oculomotor nerve arises within the Edinger-Westphal preganglionic nucleus. Axons of postganglionic cells of the ciliary ganglion innervate the sphincter pupillae muscle of the iris (for pupillary constriction) and the ciliary muscle (for close to imaginative and prescient accommodation) (Table 29. The preganglionic parasympathetic fibers of the facial nerve originate in the superior salivatory nucleus. Some of those fibers course via the greater petrosal nerve to terminate in the pterygopalatine ganglion, which provides the lacrimal gland and nasal and palatal mucous glands. Other preganglionic fibers journey through the chorda tympani to the submandibular ganglion, which innervates the submandibular and sublingual salivary glands (Table 29. The glossopharyngeal nerve accommodates preganglionic parasympathetic fibers that originate within the inferior salivatory nucleus. These fibers take a tortuous course, through the tympanic nerve and plexus, to kind the lesser petrosal nerve, which ends in the otic ganglion. Postganglionic fibers from the otic ganglion be part of the auriculotemporal nerve to attain the parotid gland (Table 29. The visceral motor component of the vagus nerve offers parasympathetic innervation to organs of the thoracic and abdominal cavities. A few, nonetheless, specifically people who innervate the guts, arise in the nucleus ambiguus, although this nucleus is extra commonly related to somatic efferent neurons whose axons journey in the glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves to skeletal muscle targets in the palate, pharynx, and larynx. Preganglionic fibers of the vagus nerve terminate on postganglionic neurons of intramural ganglia situated in the walls of viscera within the thorax and abdomen (Table 29. The sacral component of the parasympathetic division innervates the lower digestive tract (beginning simply proximal to the left colic flexure) and the urinary bladder, urethra, and reproductive organs. Preganglionic fibers exit the spinal cord via anterior roots and kind the pelvic nerves (nervi erigentes). These nerves mingle with sympathetic fibers of the inferior hypogastric plexuses to kind the pelvic visceral plexus lateral to the rectum, bladder, and uterus (Table 29. Both preganglionic and postganglionic parasympathetic neurons release molecules along with the principal transmitter at their terminals. These embody neuropeptides, most prominently vasoactive intestinal peptides, which act as modulators of the postsynaptic response to the primary transmitter. Muscarinic cholinergic receptors appear to be the one class involved within the response of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glandular cells to acetylcholine. For instance, parasympathetic stimulation of gastric acid secretion is mediated by M1 muscarinic receptors, whereas M2 receptors mediate parasympathetic despair of coronary heart rate and contraction of cardiac muscle. The cholinergic receptor blocker atropine has effects which are clinically useful in certain circumstances. These effects embrace pupillary dilation, relaxation of bronchiolar muscle, and reduction of peristalsis and secretion within the abdomen. The enteric nervous system is regarded by some authorities because the third division (along with the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions) of the autonomic nervous system. Distention of the intestinal lumen by a bolus of ingested material prompts an elaborate intrinsic network that features sensory neurons, motor neurons, and several types of interneurons. More than a dozen distinct useful forms of intrinsic neurons have been recognized, including several kinds of sensory neurons (mechanoreceptors, chemoreceptors, nociceptors), interneurons (excitatory, inhibitory, orally projecting, caudally projecting), and motor neurons (secretomotor, excitatory and inhibitory muscle motor). These cells have in depth connections each with each other and with typical easy muscle cells, that are themselves electrically coupled. Although this ongoing wave sample of electrical exercise of smooth muscle is an intrinsic property of the gut wall, input from the enteric nervous system is important to translate the slow waves of depolarization into functionally helpful waves of contraction. The peristaltic reflex could be initiated both when the presence of a meals bolus distends the intestinal wall and prompts intrinsic mechanoreceptive sensory neurons or when the enteroendocrine cells in the lining epithelium reply to contents within the lumen by activating chemoreceptive sensory neurons. Excitatory interneurons activate excitatory motor neurons upstream from the bolus and inhibitory motor neurons downstream from the bolus. In addition to intrinsic reflex pathways that coordinate peristaltic waves, further native neural circuits bring about reflexive modifications in other activities, corresponding to absorption, local blood flow, and secretion. Reflex-mediated secretion is initiated within the epithelium by enteroendocrine cells that monitor the chemical composition of the luminal contents and activate sensory neurons. The sensory neurons then activate secretomotor pathways that result in acceptable secretions by glandular cells.
Syndromes
- Infection
- Scarring of the tympanic membrane
- Low urine output (a sign of decreasing kidney function)
- Has the baby (child) always been a fussy eater?
- Dry mouth, when the glands that produce saliva are destroyed (see: Sjogren syndrome)
- Many household products are made of toxic chemicals. It is important to read and follow label instructions, including any precautions.
Tolterodine 4 mg order overnight delivery
Condyloid joints have a concave aspect articulating with a convex floor allowing flexion, extension, adduction, and abduction, for example, in the tibiofemoral joints of the knee and the radiocarpal joint of the wrists. Small joints in the hands and ft sometimes have a saddle type and allow related directions of movement because the condyloid joints. In this text, we talk about the development, anatomy, and performance of the synovial joints; the principle ailments affecting the joints; and provides some insights into the quickly developing features of joint-repair strategies. Most data available provide insights into the developmental processes of the completely different skeletal parts and the molecular elements of chondrogenesis and osteogenesis. This data is especially related because it offers a basis to better understand the molecular background of widespread joint problems and diseases, as well as genetic syndromes related to joint malformations. Part of joint development in particular the formation of the joint surface, the articular cartilage, and subchondral bone, is a postnatal and not a fetal event (Table 13. The articular surfaces are related by the synovium that consists of a thin pseudoepitheloid lining layer and a free connective tissue sublining zone. The enthesis is an anatomic area referring to the insertion of tendons and ligaments within the underlying bone. Images of the synovium, the articular cartilage and the enthesis are further enlarged. Joints and extra bones shall be fashioned concomitantly during fetal life and postnatal development. The skeletal parts and the joints are derived from cell populations denominated as osteochondroprogenitor cells. However, as these cells also contribute to the development of different tissues, such as the synovium, the ligaments, and tendons; it was proposed to call them skeletogenic cells. Patterning genes, such as the Hox (Homeobox) cluster outline the position of the totally different skeletal elements10,11 and master swap transcription factors, corresponding to Sox9 (Sry-box containing gene 9) and Runx2 (runt related transcription issue 2) steer chondrogenesis and osteogenesis, respectively. Growth of the differentiating anlagen occurs by way of shaping of the growth plate in the small diaphysis and later on in the epiphyses. The central diaphysis incorporates the first ossification center whereas the epiphyses turn into the secondary ossification facilities. Gap junctions, specialized intercellular communication pores that allow the transport of inorganic ions and small hydrophilic molecules instantly from cell to cell, join the interzone cells. Homozygous null embryos show anterior-posterior axis formation anomalies, however develop to e7. Multiple conditional mutations have shown defects in distinct stem cell sorts that end in proliferation defects, corresponding to intestinal polyps, brain, and spinal wire measurement anomalies, etc. Homozygotes for null mutations exhibit barely shortened long bones of the limbs, and drastically shortened bones of the feet, with some full or partial fusions. Wnt9a 602863 Wnt16 -Catenin none recognized Colorectal cancer Hepatoblastoma Hepatocellular carcinoma ovarian most cancers Pilomatricoma acromesomelic dysplasia Hunter�Thompson kind Brachydactyly, kind C Chrondrodysplasia, Grebe kind Fibular hypoplasia and complicated brachydactyly Symphalangism, proximal Multiple synostoses syndrome 2 osteoarthritis klippel�Feil syndrome 1, autosomal dominant Microphthalmia, isolated four Brachydactyly, type B2 Multiple synostosis syndrome 1 Stapes ankylosis with broad thumb and toes Symphalangism, proximal Tarsal�carpal coalition syndrome none recognized 606267 116806 Gdf5 601146 Gdf6 Homozygous null mice present a quantity of joint and skeletal patterning defects affecting the extremities, inside ear, and skull. Homozygotes for a focused null mutation exhibit failed closure of neural tube, exencephaly, wide club-shaped limbs, loss of tail vertebrae, shortened physique axis, irregular cartilage condensations, and lethality at start. Homozygous null mice fail to breathe and die at birth exhibiting a slender thoracic cage, irregularly mineralized sternum, cleft secondary palate, and delayed bone mineralization. Homozygotes for null mutations exhibit cardioskeletal myopathy, cardiac blockage, delayed progress, and early postnatal lethality. For instance, Hoxa genes appear to decide skeletal components along with the proximodistal axis whereas Hoxd genes outline the place along with the anteroposterior axis in the limb. Chondrocytes hold proliferating and give rise, layer by layer, to maturing chondrocytes. The mesoderm has shaped the notochord and is starting to type lateral plate and paraxial derivatives on either sides of the midline. Less is understood concerning the supply of the cells that will kind the opposite tissues of the joint, such because the synovium and the ligaments. Finally, the cavitation course of takes place with bodily separation of the cartilaginous element. Concomitant with that process, Sox9 is repressed and -catenin induced in hypotrophic chondrocytes. Arrows up, induction; arrows down, repression; black (blue within the web version) ovals, Sox9 positive cells; mild grey (blue/red in web version) ovals, Sox9 and -catenin optimistic cells; gray (red within the web version) ovals, -catenin positive cells. However, these data nonetheless need to be corroborated in in vivo techniques to totally define the extent of the function of those integrins. Cell demise was thought for an extended time as an important issue but this hypothesis has not been convincingly demonstrated as 2.
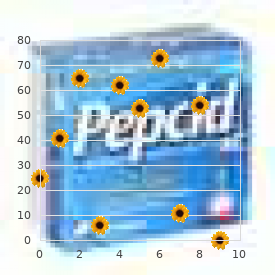
Tolterodine 2 mg purchase on-line
Novel Itch Pathway Microneurographic recordings in human single-nerve fibers have recognized a unique histamine-selective C fiber population that conducts itch sensations. Itch receptors show large receptive fields (85 mm2 on the lower leg), and the fibers are slowly conducting (0. A distinct population of histamine-responsive second-order cells in lamina I of the posterior horn was identified as part of the central neural substrate for itch notion. Neural activity within the thalamus associated with pain was significantly larger than that associated with itching. No noticed significant difference in activity between itching and pain within the presupplementary motor space, the bilateral anterior insula, the anterior cingulate cortex, or the basal ganglia was famous. Thus there are vital differences in the central processing of data associated to the sensations of itch and pain. On the premise of the localization of putative neurotransmitters and secondary messengers in the posterior horn, a number of candidates, corresponding to peptides (calcitonin gene�related peptide, substance P), glutamate, and nitric oxide, may be involved on this process. These and other chemical brokers underlie the central pharmacology of nociceptive transmission and are answerable for the various qualities related to central ache pathways. Pain can be categorised as acute or continual, quick or gradual, boring or sharp, and burning, throbbing, or aching. Because ache is such a posh sensory experience, reduction or elimination of nociceptive sensations is of obvious medical significance. Effective clinical approaches that can be used for the aim of controlling ache embody pharmacologic intervention, cognitive behavioral therapy, and stimulation-produced analgesia. They are capable of controlling nociceptive neuron firing and are delicate to opiates. Hypothalamospinal fibers additionally project to the intermediolateral cell column of the higher thoracic twine ranges. As famous previously, endogenous opiates such as enkephalin inhibit ache transmission. Systemic administration of pharmacologic opiates, similar to morphine, excites periventricular and periaqueductal neurons, supplementing their natural exercise. This increase in activity suppresses neurons within the spinal and medullary posterior horns that transmit painful information, also producing analgesia. The direct supply of opioids to the spinal cord (epidural anesthetic techniques) is also used to produce a powerful analgesia for surgical procedures and deliveries. Current therapies for the management of pain transmission embody transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation and chronic stimulation of the posterior columns by implanted electrodes. These collaterals stimulate the enkephalinergic interneurons within the posterior horn that inhibit the transmission of ache signals. This stimulation also supplies long-term diminution of ache for causes that are poorly understood. Acupuncture-like stimulation also might produce native analgesia by stimulating these fibers. This elevated exercise is particularly prevalent in the somatosensory cortex and the frontal cortex. In addition to raphespinal and ceruleospinal fibers, some reticulospinal fibers additionally affect pain transmission within the posterior horn. This widespread cortical activation could provide a morphologic basis for integrating the situation of painful stimuli with memory and emotion. Similar increases in cortical activation in the posterior insula and anterior cingulate cortex in addition to within the cerebellar vermis have been described for both sexes. However, will increase in the contralateral prefrontal cortex exercise, contralateral insula, and thalamus famous in feminine topics counsel that pain perception and processing may be completely different in males and females. These varied methods are offering a extra full identification of buildings included in ache pathways and are liable for the processing of painful stimuli. The Initial Processing of Pain and Its Descending Control: Spinal and Trigeminal Systems, Vol 12. Pain reduction by focal electrical stimulation of the mind: an anatomical and behavioral evaluation. Gender differences in ache notion and patterns of cerebral activation during noxious warmth stimulation in people. A research of the functional contributions of the lemniscal and spinothalamic techniques to somatic sensibility: central nervous mechanisms in ache. The Pain System: the Neural Basis of Nociceptive Transmission in the Mammalian Nervous System, Vol.
Discount 2 mg tolterodine amex
Sounds are transmitted throughout the space from the tympanic membrane to the fluid-filled internal ear by a series of three bony ossicles: the malleus, incus, and stapes. On one end of this chain, the arm of the malleus is attached to the tympanic membrane, and on the different finish, the footplate of the stapes suits into the oval window on the interface with the fluid-filled vestibule of the internal ear. The three bones act as levers to reduce the magnitude of movements of the tympanic membrane whereas rising their force at the oval window. In this way, air stress waves putting the tympanic membrane lead to plunger-like movements of the stapes in opposition to the oval window that have the necessary pressure to produce fluid stress waves within the cochlea. Its major elements include a labyrinth of fluid-filled canals, specialised sensory epithelium of the organ of Corti, and neurons of the spiral ganglion with their peripheral and central axonal branches. The canals of the osseous and membranous labyrinth of the cochlea spiral two- and two-third turns from base to apex over a length of 34 mm. Uncoiled, the outer canals of the osseous labyrinth resemble a U-shaped tube and thus essentially are one canal. Scala tympani, the lower chamber in cross part, is continuous with the upper chamber at a hair pin curve, the helicotrema, on the apex of the cochlea. The fluid with which the vestibule and scala vestibuli and tympani are crammed is perilymph. It comprises the membranous labyrinth and at its base is related by ductus reuniens to the saccule of the vestibular membranous labyrinth. The basilar membrane, extending from the spiral osseous lamina of the modiolus (as from threads of a screw) to the spiral ligament on the outer wall of the canal, is the decrease boundary separating the scala media from scala tympani under. The endolymph, which fills the cochlear duct, is elaborated by the cells and rich capillary bed of the stria vascularis. The blue and pink strains represent the spiral course of scala vestibuli and scala tympani, respectively, from base to apex of the cochlea. C, the basilar membrane features to separate waves of various frequencies within a sound. This membrane is narrow and stiff at its base and becomes wider and more versatile towards the apex, and the hair cell stereocilia enhance correspondingly in height. These features "tune" the membrane so that every frequency of sound within the audible vary will trigger a wave in the basilar membrane that has its peak amplitude at a unique spot (near the bottom for prime frequencies and close to the apex for low frequencies). At this spot, the hair cells are excited most intensely, producing a peak in neural output. Note that the designation lateral or medial olivocochlear efferents refers to their origin within the superior olive, not to their goal in the organ of Corti. It consists of internal and outer hair cells, supporting cells, and the tectorial membrane. This tunnel is shaped by the filamentous arches of the inside and outer pillar cells and is filled with fluid much like perilymph. It is unsure how lots of the inside (about 3500) or outer (about 12,000) hair cells have to be misplaced to illness, trauma, or getting older earlier than a just-noticeable sensorineural hearing loss ensues. The taller stereocilia in every hair bundle are in contact with or embedded within the tectorial membrane. Consequently, movement of the basilar membrane and the organ of Corti will bend the stereocilia against the tectorial membrane and cause a graded depolarization of the hair cells. At their apical surface and hair bundle, inside 310 Systems Neurobiology hair cells are bathed in endolymph. Endolymph, like intracellular fluid, has a excessive focus of potassium and low concentration of sodium ions. At the basilar membrane inside hair cells oppose the perilymph-filled scala tympani. In contrast to endolymph, perilymph, like cerebrospinal fluid, has a high concentration of sodium and low focus of potassium ions. This endolymphatic potential seems to be as a outcome of the selective secretion and absorption of ions by the stria vascularis. As the basilar membrane strikes up in response to fluid movement within the scala tympani, the taller stereocilia are displaced towards the tectorial membrane. Damage to the stria vascularis ends in lack of the endolymphatic potential and failure of mechanoelectrical transduction.
4 mg tolterodine
The cochleotopic order and thus tonotopic illustration are highly conserved all through the auditory pathways. When outer hair cells depolarize, adjustments in conformation of lateral membrane proteins result in modifications in the peak of the cells and stiffness of their stereocilia. These physical changes successfully impart energy to movement of the basilar membrane, thereby enhancing sensitivity and precision of tuning of inside hair cells. Frequency is coded within the cochlear nerve by the position of afferent fibers along the cochlear spiral. As the depth of the sound drops to near threshold, the frequency response range narrows. The attribute frequency is the frequency at which the fiber has the bottom threshold. For low-frequency fibers, the timing of every impulse is phase locked with the stimulus cycle, so that the fiber output preserves the timing information of the signal. Intensity is coded each by the discharge price of cochlear nerve fibers and by recruitment of exercise in additional afferents as stimulus intensity will increase. At higher stimulus intensities, further cochlear nerve fibers having sequentially greater thresholds are recruited. Sensorineural Deafness Sensorineural deafness (this could sometimes be known as nerve deafness) results from damage to the cochlea or to the cochlear root of the vestibulocochlear nerve. The causes of sensorineural deafness are various and will embrace repeated publicity to loud noises, remedy with certain antibiotics, infections (such as rubella, mumps, or bacterial meningitis), and tumors at different levels of the neuraxis. As is the case with the center ear, trauma within the type of cranium fracture may end in sensorineural deafness. The deficits experienced by the affected person are deafness in the ear on the affected aspect, various levels of tinnitus, a perception of ringing in the ears if the cochlea is broken, and extra signs and symptoms indicative of injury to the adjacent vestibular root. Immediate sensorineural hearing loss may occur after even a single exposure to a sudden loud blast. Frequency tuning curves (A), poststimulus time histogram of discharges via the period of a tone burst on the attribute frequency of a major afferent fiber (B), and rate-intensity curve illustrating how a limited range of intensity can be coded within the response of main afferent fibers to growing depth of a tone at its characteristic frequency (C). To take a look at bone conduction, a vibrating tuning fork (256- or 512-Hz frequency) is placed immediately on the vertex of the cranium or the mastoid process. Perceiving these vibrations as sound signifies that the sound (or vibration) bypasses the exterior and middle ear and is transmitted by way of bones of the cranium directly to the cochlea in the internal ear. Perception of the vibration (sound) requires that the sound waves generated be transmitted throughout the tympanic membrane and the ossicles of the center ear to attain the oval window and cochlea; disease or damage in either the exterior or the middle ear would lead to diminished or absence of listening to on this ear, referred to as a conductive listening to deficit. Ideally, both the Weber take a look at and the Rinne take a look at ought to be administered to every patient, and the observations from the Weber test ought to correlate with these of the Rinne test. That the sound can be perceived as louder in the faulty left ear seems paradoxical but, though not absolutely understood, is probably as a result of masking of ambient room noise in the left ear. The tuning fork is then turned and placed in front of the exterior acoustic meatus of the left ear. With regular listening to (positive Rinne), air conduction is louder (and longer) than bone conduction. It can also be famous in the Rinne take a look at that the period of audible sound is often longer for air conduction than for bone conduction. The findings for normal listening to and for conductive listening to loss reflect the effectivity of conduction of sound from air to fluid by the center ear. Sound was not perceived by air conduction when sound perception by bone conduction ceased. This indicated the presence of either a conductive deficit within the left ear or a sensorineural deficit in the right ear. Within this tonotopic framework, projections connect related frequency regions of successive nuclei. Information processing is subsequently hierarchical with increasing complexity of feature extraction. As cochlear information ascends to the auditory cortex, info is distributed via multiple parallel pathways that ultimately converge within the inferior colliculus. The hierarchy of auditory nuclei involved in these parallel pathways contains the cochlear nuclei, nuclei of the superior olive and trapezoid physique, nuclei of the lateral lemniscus, and inferior colliculus.
Giores, 63 years: The cleft matrix accommodates a basal lamina with collagen and laminin that mix to maintain the nerve and muscle in close approximation and exact register during the active muscle activity. In studies that embody collection of parturition and lactation data, several different measurements could also be taken for the neonates (or juveniles). Molecular and mobile characterisation of extremely purified stromal stem cells derived from human bone marrow. From a few dozen cells that together weigh perhaps a microgram, the brain becomes an organ weighing about 800 g at birth, 1200 g at 6 years of age, and about 1400 g within the adult-about a billion-fold increase.
Rune, 65 years: Ly2439821, a humanized anti-interleukin-17 monoclonal antibody, in the treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a part I randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, proof-of-concept study. Osteoblasts entrapped in the bone matrix, morph into osteocytes, which communicate with each other and the bone surface through cytoplasmic projections. Treatment with Wnt inhibitors in animals with actively rising bones leads to a lower in ossification beneath the growth plate, with a discount in bony trabeculae inside the metaphysis. The dissection of gene�environmental interaction results on bone phenotypes continues to be a significant challenge in genetic analysis.
Felipe, 47 years: The concept of a "synovio-entheseal complicated" and its implications for understanding joint inflammation and damage in psoriatic arthritis and past. Although rare, hydrocephalus may also be seen in patients with impaired venous circulate from the brain. Their apical dendrites ascend into layer I, and their axons descend into and thru the deeper layers. Typically, karyotyping is performed using peripheral blood leucocytes (isolated from a heparinized blood sample), that are initially cultured, prior to evaluation by highresolution G-banding (Giemsa staining) of at least 20 metaphase nuclei.
Daryl, 23 years: However, reviews also point out situations by which healthy people with in any other case normal olfactory acuity are unable to understand the odor of a selected compound or class of compounds. Immunohistochemical detection of parathyroid hormone-related protein in human fetal epithelia. The ectomeninx around the brain is steady with the skeletogenous layer that varieties the skull. Threshold Voltage Repolarization the lifetime of the open sodium channel is restricted to a number of milliseconds.
Shakyor, 26 years: Their abundance and strategic location within the core of the lacuna�canalicular community make these cells probably the most suitable candidates for detecting variations within the degree of strain and for distributing indicators leading to adaptive responses. Purkinje cell Granule cell Mossy fiber Climbing fiber Subcortical white matter the fastigial, globose, and emboliform nuclei; and most areas of the dentate nucleus and the superior and center cerebellar peduncles. Common examples embody the central nervous system (hydrocephalus, macrocephaly, microcephaly, spina bifida); coronary heart (ventricular septal defects); kidney (renal agenesis); and limbs (arthrogryposis, fractures secondary to osteogenesis imperfecta). Septic emboli may infect and weaken the vessel wall itself, leading to a mycotic aneurysm.
Moff, 40 years: Areas 3b and 1 lengthen up the financial institution of the sulcus onto the shoulder of the postcentral gyrus, whereas space 2 lies on the gyral floor and abuts area 5 (somatosensory affiliation cortex). In addition to the actions of those pathways, the dopaminergic loop from the neostriatum to the substantia nigra and again to the neostriatum can additionally be lively. As a result, the relay of information via the hippocampal formation is impeded. The spinal trigeminal tract consists of central processes of major sensory fibers that enter the brain mainly in the trigeminal nerve.
Baldar, 36 years: More substantial reactions representing an escalation of synovitis to arthritis are related to extension of the inflammatory process into the periarticular soft tissues and/or a considerable inflammatory cell inflow into the joint area or different intraarticular tissues. In protocols for bone regeneration, there are additional considerations: (1) autologous (self) versus allogeneic (nonself); and (2) embryonic origin of the bone. Allocation into the osteoblast or adipocyte lineage is dictated by a quantity of transcription elements, which in 2. The neuronal and astrocytic pathways interact, and each are regulated by oxygen tension.
Tippler, 29 years: C and D, Electron micrographs of a myelinated fiber (C) and an unmyelinated fiber (D) composed of a single Schwann cell supporting greater than 20 axons. This system includes constructions that obtain inputs from diverse areas of the neuraxis and take part in sophisticated and interrelated behaviors such as reminiscence, learning, and social interactions. Pattern recognition for the prognosis of inflammatory conditions in the pores and skin was pioneered by A. In about 80% of people, the two thalami fuse throughout the third ventricle to type the interthalamic adhesion (massa intermedia).
Kaelin, 62 years: Third, a persistent ostium primum outcomes from incomplete fusion of the primary septum and the endocardial cushions, with resultant anomalies in the atrioventricular valves. As there are 31 spinal cord ranges (8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, 1 coccygeal), so are there 31 corresponding pairs of spinal nerves. Shown here is the crystallographic structure of a channel that could probably be a homotetramer of and subunits. These fibers originate from various hypothalamic nuclei and project primarily to corticomedial nuclei of the amygdaloid complicated.
Peer, 59 years: These embrace constriction of the pupil (miosis) brought on by the unopposed action of the parasympathetically innervated sphincter pupillae, drooping of the higher eyelid (ptosis) ensuing from paralysis of the superior tarsal muscle (of M�ller), flushing of the face from loss of sympathetically mediated vascular tone, and diminished or absent sweating (anhidrosis) on the face. The peripheral branch programs as part of a peripheral nerve to convey sensory info from a somatic or visceral structure, such as the skin, skeletal muscle, or wall of intestine. The segmental branches that serve the posterior and anterior roots and the posterior root ganglia are the radicular arteries, and branches that largely bypass the roots to supplement the blood supply to the twine are the spinal medullary arteries. The narrowest a part of the channel excludes larger molecules; the inner structure has a excessive dielectric that effectively substitutes for bulk water, allowing single water molecules to corkscrew via the channel.
Derek, 45 years: Chondromalacia is the macroscopic term used to describe rubbery articular cartilage. The mechanism by which divalent cations like calcium modify the excitability of nerves is subtle and is intently related to the detailed construction of the membrane lipid bilayer. The sigmoid sinus is giant and represents an essential route for venous drainage from the brain. The Cerebral Cortex of Man: A Clinical Study of Localization of Function [facsimile of 1950 edition].
Tuwas, 46 years: The rostral opening, the anterior neuropore, closes at about 24 days, and the caudal opening, the posterior neuropore, closes about 2 days later. There is an intimate relationship of neural tissue to the encircling bone, meninges, muscle tissue, and skin. Treatment of symptomatic cartilage defects of the knee: characterised chondrocyte implantation results in better clinical consequence at 36 months in a randomized trial in comparability with microfracture. They shuttle nutritive molecules from blood vessels to neurons, remove waste products, and preserve the electrochemical surroundings of neurons.
Leon, 42 years: For instance, a definite chance is that common variants related to variations in height30 modulate the pathways underlying chondrocyte hypertrophy in the development plate. Destructive static checks, the place the drive is utilized slowly and steadily until the bone breaks, are most commonly used for animal models and drug testing. In D, results of Rinne testing in the right ear point out that each air and bone conduction are diminished, which suggests a sensorineural hearing loss (in the right ear). The preliminary discovering is a dilated pupil (pressure on the third nerve) on the facet of the herniation, followed by a paralysis of most eye movement within the eye with the dilated pupil.
Milok, 38 years: Given the progressive growing older of the final population and the paucity of medication to deal with or prevent the age-related decline in cognition this could be a question of crucial importance. As noted earlier, the unipolar brush cell is essentially unique to the granular layer of the vestibulocerebellum and is involved within the cerebellar and vestibular regulation of eye movement. Multistage genome-wide affiliation meta-analyses identified two new loci for bone mineral density. On the premise of their afferent and efferent connections, these three bigger cortical zones could be subdivided additional into 9 smaller zones.
Asaru, 39 years: Many challenges lie ahead, particularly within the space of information interpretation (informatics), which often involves database searching, segregation evaluation, bioinformatic prediction, and practical demonstration. Tanycytes have basal processes that extend by way of the layer of astrocytic processes to form end-feet on blood vessels and in the neuropil. Other astrocyte merchandise, similar to cholesterol and lipoproteins, are additionally thought to improve synaptic plasticity. Experiments targeted on this issue demonstrated that the patterns of actions required to perform previously discovered advanced volitional motor duties might be recalled in the course of the inactivation of the ipsilateral dentate and interposed nuclei.
Anog, 41 years: The rubrospinal system is influenced by the cerebral cortex and the cerebellar nuclei via corticorubral (uncrossed projection) and cerebellorubral (crossed projection) fibers, respectively. Other essential telencephalic constructions in the domains of P3 and P4 include the parahippocampal gyrus and the precuneus. Hypothalamic neurons that reply to these changes by altering their firing charges are considered to be the "receptor" cells. Within this nucleus, neurons projecting to the dorsal vagal nucleus and the nucleus ambiguus respond in a way opposite to that of neurons projecting to the rostral elements of the anterolateral medulla.
Tarok, 61 years: The taller stereocilia in every hair bundle are involved with or embedded in the tectorial membrane. The website at which an axon terminal communicates with a second neuron, or with an effector tissue, is called a synapse (from the Greek word that means "to clasp"). Severe osteoporosis in mice lacking osteoclastogenesis inhibitory factor/osteoprotegerin. Normally, cortical axons release glutamate as their neurotransmitter within the caudate and putamen.
Kamak, 31 years: Instead late in embryogenesis xenobiotic exposures are extra probably to cause functional deficits and intrauterine development retardation. Teratogens typically have an effect on a number of species, and induce an analogous spectrum of effects across delicate species. The first in vivo information to suggest that bone regulates muscle mass and function was in 2015 exhibiting that osteocalcin partially restored muscle mass in a model of deletion of cx43 in osteocytes151 and these effects of osteocalcin on muscle have been repeated and extended by the Karsenty laboratory in 2016. The fibers that carry visual information from the decrease quadrant of the contralateral hemifields originate from the dorsomedial portion of the lateral geniculate nucleus, arch instantly caudally to pass through the retrolenticular limb of the internal capsule, and synapse within the cortex of the superior bank of the calcarine sulcus, on the cuneus.
Vibald, 58 years: This osmolarity is essentially a operate of how much water is retained throughout the body. In addition, this cell group, particularly its central nucleus, receives ascending enter from nuclei within the brainstem known to be concerned in visceral capabilities. The Cell Biology of Neurons and Glia 33 Peripheral nerve Perineurium Endoneurium Unmyelinated axons Lightly myelinated axons Epineurium Schwann cell: Cytoplasm Basal lamina Heavily myelinated axon A Axon Endoneurium Epineurium Perineurium Basal lamina of perineurial cells Collagen Endocytotic vesicles Axon Collagen the chance of axonal regeneration is best when a peripheral nerve is compressed or crushed however not severed. Research using the model trait of top provides insights as to the probably repositories of unmapped genetic variants.
10 of 10 - Review by V. Sancho
Votes: 333 votes
Total customer reviews: 333
References
- Ueno M, Nakashima O, Mishima M, et al. Pulmonary glomus tumor: CT and MRI findings. J Thorac Imaging 2004;19(2):131-4.
- Menzies SM, Rahman NM, Wrightson JM, et al: Blood culture bottle culture of pleural fluid in pleural infection. Thorax 66(8):658-662, 2011.
- Huang JQ, Sridhar S, Hunt RH. Role of Helicobacter pylori infection and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in peptic-ulcer disease: a meta-analysis. Lancet 2002;359:14.
- Gettman, M.T., Lotan, Y., Napper, C.A., Cadeddu, J.A. Transvaginal laparoscopic nephrectomy: development and feasibility in the porcine model. Urology 2002;59:446450.
- Fyfe AI, Huckell VF, Burr LH, Stonier PM. Leiomyosarcoma of the left atrium: case report and review of the literature. Can J Cardiol 1991;7:193- 196.