Angela Cheng-Lai, PharmD
- Department of Pharmacy
- Montefiore Medical Center
- Department of Medicine
- Albert Einstein College of Medicine
- Bronx, NY
Geodon dosages: 80 mg, 40 mg, 20 mg
Geodon packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 360 pills

Geodon 20 mg discount visa
The mountain and valley sample seen in seborrheic keratosis is within the dermoscopic differential diagnosis. A positive wobble sign by which the delicate nevus moves from side to aspect with motion of instrumentation versus a stiff immoveable seborrheic keratosis helps to make the differentiation. Local standards consists of; irregular pigment network (red arrows), irregular dots and globules (circles), irregular blotches (black arrows) and blue-white colour (stars). Peppering (yellow box) and grey blotches (yellow arrows) are a half of the regression. There is asymmetry of colour and structure (+) plus the multicomponent international pattern (1,2,3). Local standards consists of; irregular dots and globules (circle), blue-white color (stars) and peppering (boxes). There is an atypical starburst (spitzoid) international sample with foci of streaks at the periphery (boxes). Local criteria contains; irregular dots and globules (circles), irregular streaks (boxes) and regression. Typical glomerular vessels (black box) and large dotted vessels (yellow box) help diagnose this nonspecific pink scaly patch. The gray dots represent melanophages and free melanin in the papillary dermis, not atypical melanocytes. A sub-set of lichen planus-like keratosis are thought to characterize an immunologic event against flat seborrheic keratosis of solar lentigines. The lesion is suspicious clinically but has a differential diagnosis that includes a seborrheic keratosis. There is asymmetry of color and structure, asymmetrical pigmentation (black arrows) around follicular openings (red arrows), annular-granular constructions (circles) and irregular blotches (boxes). Different colors plus blood pebbles (boxes) characterize this posttraumatic lesion. The brown (red arrows) and purple blotches (white arrows) outcome from the breakdown of blood. Terminal hairs with perifollicular hypopigmentation (boxes), atypical pigment community (circles) and regular globules (arrows) characterize this small congenital melanocytic nevus. There are different shades of pink shade, pinpoint (boxes) and comma shaped vessels (yellow arrows) plus a milky-red area (black arrow). There are foci of irregular dots and globules (boxes), irregular blotches (black arrows) and multifocal hypopigmentation (red arrows). A central common blotch (stars) plus globules (black arrows) and some streaks (red arrows) in any respect points of the periphery characterize this classic starburst/spitzoid pattern. There is asymmetry of shade and structures (+), the multicomponent international pattern (1,2,3), irregular pigment network (black box), irregular dots and globules (circles), irregular blotches (yellow arrows), and reticular depigmentation (white box). There is an absence of melanoma specific criteria found on the face with totally different shades of pink and brown color plus ulceration (yellow arrows). A rapidly growing nodule (arrow) representing a squamous cell carcinoma and the mountain and valley sample of a seborrheic keratosis (box) characterize this lesion. There are excessive risk standards on the periphery of the lesion which might be exhausting to determine B. There are criteria for a seborrheic keratosis or basal cell carcinoma related to pigment network and brown globules C. There is an absence of standards to diagnose a melanocytic lesion, seborrheic keratosis, dermatofibroma, pyogenic granuloma or ink-spot lentigo, subsequently the lesion ought to be thought-about melanocytic D. There is an absence of standards to diagnose a melanocytic lesion, seborrheic keratosis, basal cell carcinoma, dermatofibroma or hemangioma, subsequently the lesion should be considered melanocytic E. Fissures, ridges, sharp border demarcation, milialike cysts, follicular openings, fats fingers and hairpin vessels D. The absence of a pigment community, arborizing vessels, pigmentation, ulceration, spoke-wheel constructions D. A variable number of pink, sharply demarcated vascular areas called lacunae and fibrous septae C. Multifocal hypopigmentation, arborizing vessels and a central bluish-white veil 7. Melanoma-specific standards on the trunk and extremities can include this mixture of criteria: A. Asymmetry of colour and structure, a cobblestone international pattern and regular globules or blotches B.
Purchase geodon 80mg with visa
E: the ischial backbone should be only somewhat (if any) more prominent than on the alternative side. Fixation Loss of rotation Nonunion Implant removal In smaller youngsters, threaded pins can be utilized as an alternative of screws. It is important to have a minimal of three factors of fixation in the ilium to prevent postoperative movement and rotation. To prevent this we regularly add a pubic ramus screw and exchange any excised bone again into the osteotomy sites. Leaving the implants barely prominent or attaching a nonabsorbable suture to the screw head on one finish and to the subcutaneous tissues on the opposite facilitates later implant removal. If sufficient bone healing is noted on radiography, exercise can then be advanced as tolerated. The fixation screws may be removed 6 to 12 months postoperatively (if you have chose to remove them). Whether the screw presence will hinder or compromise a later total hip alternative stays unclear. Clearly, femoral implants must be eliminated, but some consider acetabular screw removal less essential. We lean toward removal of all implants from the hip in these patients, as they could require a later whole hip substitute. Ten hips improved radiographically, eight improved functionally, and one required total hip arthroplasty. At a mean 9-year follow-up, 12 (20%) hips had been transformed to whole hip arthroplasty and 4 (7%) hips had incapacitating ache. There also was a statistically vital relationship between failure of the osteotomy and severity of pre-existing hip arthrosis. When evaluating any procedure, you will want to consider the quality of every individual procedure, which is difficult to do within the literature. We have found by way of our personal expertise that the quality of the surgical procedure and the anticipated outcomes enhance dramatically with surgeon expertise. In sufferers with acetabular dysplasia, indications and outcomes are higher understood. Pre- and postoperative three-dimensional computed tomography analysis of triple innominate osteotomy for hip dysplasia. A new periacetabular osteotomy for the remedy of hip dysplasias: method and preliminary results. Legg-Calv�-Perthes disease, half I: classification of radiographs with use of the modified lateral pillar and Stulberg classifications. Evaluation of the biomechanics of the hip following a triple osteotomy of the innominate bone. Location of acetabular deficiency and associated hip dislocation in neuromuscular hip dysplasia: three-dimensional computed tomographic analysis. Protein C ranges in sufferers with Legg-Calv�-Perthes disease: is it a real deficiency Pericapsular osteotomy of the ilium for the remedy of congenitally dislocated hips. Triple innominate osteotomy in younger adults for the treatment of acetabular dysplasia: a 9-year follow-up research. Growth and improvement of the acetabulum within the normal child: anatomical, histological, and roentgenographic studies. A comparability of the fixation stability of multiple screw constructs for two forms of pelvic osteotomies. The objectives are improved femoral head coverage, a steady articulation, and metaplastic transformation of the hip capsule to fibrocartilage to create a secure, pain-free hip. Contraindications embody extreme arthrosis, age larger than 45 (relative, the place arthroplasty may be a greater option), and important proximal migration of the femoral head (may prevent enough protection by thinner proximal ilium). In instances of spastic hip dysplasia, the lateral and posterolateral acetabulum is most frequently poor. The location of acetabular deficiency have to be thought of when planning the form and orientation of the osteotomy and positioning of the iliac shelf over the hip joint.
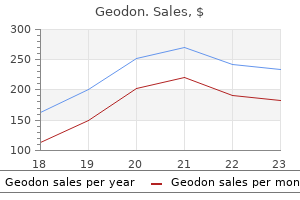
40mg geodon discount overnight delivery
The sensation of touch within the space of distribution of the nerve can be examined by touching different areas of pores and skin with a wisp of cottonwool. The facial nerve provides the muscles of the face together with the muscular tissues that shut the eyelids, and the mouth. The sensation of taste should be examined on the anterior two-thirds of the tongue by making use of substances of different tastes. Paralysis of facial nerve the consequences of paralysis are because of the failure of the muscles involved to perform their regular actions. When the facial nerve is paralysed on one aspect, probably the most noticeable feature is the loss of symmetry. Normal furrows on the forehead are misplaced because of paralysis of the occipitofrontalis. There is marked asymmetry of the mouth because of paralysis of the orbicularis oris and of muscles inserted into the angle of the mouth. Asaresult of asymmetry, the protruded tongue seems to deviate to one aspect, but is in reality in the midline. The temporal region overlies the temporal fossa current on the lateral side of the cranium. The fossa is bounded above by the temporal line and inferiorly by the zygomatic arch. The wall has an anterior wall made up mainly by the temporal surface of the zygomatic bone with contributions from the larger wing of the sphenoid and from the frontal bone. Placed over the superficial facet of the temporal fascia we see some subcutaneous muscular tissues hooked up to the auricle. These are the auricularis superior,theauricularis posterior and the auricularis anterior. A few scattered muscle fibres that run vertically over the upper part of the area are given the name temporoparietalis. Immediately in front of the exterior acoustic meatus we see the auriculotemporal nerve emerging from underneath cowl of the higher finish of the parotid gland. The nerve ascends into the temporal area and scalp and divides into branches that offer them. Just in front of the auriculotemporal nerve we see the superficialtemporalvessels. Thesuperficial temporal artery is a terminal department of the external carotid artery. The temporal branch of the facial nerve runs upwards and forwards to attain the frontalis muscle that it supplies. The posterior auricular branch of the facial nerve lies behind the auricle within the lower part of the temporal area. The zygomaticofacial nerve and the zygomaticotemporal nerve are derived from the zygomatic department of the maxillary division of the trigeminal nerve. The temporalis is among the muscles that are answerable for chewing movements (mastication). The time period infratemporal fossa is utilized to an irregular house mendacity under the lateral part of the bottom of the cranium. The medial and lateral pterygoid plates arising from the process are intimately related to buildings in the fossa. Structures in the fossa (or near it) are uncovered by removing the parotid gland and the zygomatic arch. The auriculotemporal nerve passes backwards deep to the neck of the mandible and then turns upwards to enter the temporal area. The masseteric department of the mandibular nerve passes laterally via the mandibular notch to enter the masseter muscle. The buccal nerve and artery emerging from beneath the anterior margin of the ramus of the mandible to run forwards on the buccinator muscle. The maxillary artery arises from the exterior carotid artery simply behind the ramus of the mandible. The artery runs forwards deep to the neck of the mandible to enter the infratemporal fossa (38. The higher a half of the mandibular nerve lies under cowl of the lateral pterygoid muscle. Finally the anterior division continues onto the surface of the buccinator muscle as the buccal nerve.
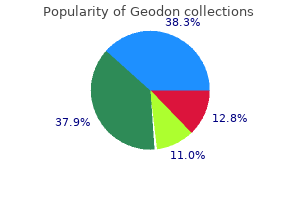
Geodon 40 mg otc
Reaching the posterior border of this muscle it curves around it and then runs forwards across the muscle. The nerve becomes superficial and divides into ascending and descending branches that supply the pores and skin on the entrance of the neck (43. The supraclavicular nerves come up (as a single ramus) from the third and fourth cervical nerves (43. Here the trunk divides into three branches referred to as the medial, intermediate and lateral supraclavicular nerves. They pierce the deep fascia slightly above the clavicle after which run downwards across this bone to reach the pectoral area. Branches arising from the ansa cervicalis innervate the sternohyoid, the sternothyroid and the omohyoid muscular tissues (viz. The superior root seems to come up from the hypoglossal nerve (hence the time period ansa hypoglossi given to the loop). However, the root is basically made up of fibres derived from the primary cervical nerve. These fibres attain the hypoglossal nerve via a speaking branch from the primary cervical nerve. Apart from forming the superior root of the ansa cervicalis, these fibres from the first cervical nerve (travelling along the hypoglossal nerve) innervate the thyrohyoid and geniohyoid muscle tissue (Also see forty three. The inferior root of the ansa cervicalis arises from the second and third cervical nerves. It descends at first lateral to the internal jugular vein and then superficial to it to be part of the superior root superficial to the frequent carotid artery. This nerve arises from the (ventral rami of) spinal nerves C3, C4 and C5 the contribution from C4 being biggest. The nerve descends vertically via the decrease part of the neck, after which via the thorax to reach diaphragm. The course and relations of the phrenic nerve in thorax are described on page 451. Crossing the medial (or lower) border of the muscle it crosses in front of the primary part of the subclavian artery (42. On the right side, nevertheless, the nerve is usually separated from the artery by a part of the scalenus anterior. Throughout its course in the neck the nerve lies deep to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. It is crossed superficially by the superior belly of the omohyoid, the transverse cervical artery and the suprascapular artery. From here the foundation descends by way of the neck lateral to the principle phrenic nerve and joins it in the upper a half of the thorax. There are twelve pairs of cranial nerves that emerge from the surface of the brain. They are recognized by quantity (in cranio-caudal sequence) and in addition bear names as follows: 2. Scheme to present the mode of innervation of the infrahyoid muscular tissues from the cervical plexus Some relationships of the phrenic nerve Chapter forty three Nerves of the Head and Neck 875 four. The third cranial nerve is known as the oculomotor nerve because it provides a quantity of muscle tissue that transfer the eyeball (Ocular = pertaining to the eye). It is so called because it provides a muscle (superior oblique) that passes by way of a pulley (trochlea = pulley). The fifth cranial nerve is recognized as the trigeminal nerve as a result of it has three main divisions. The seventh cranial nerve is the facial nerve as a result of it supplies the muscular tissues of the face. The eighth cranial nerve is called the vestibulocochlear nerve as a result of it supplies constructions in the vestibular and cochlear components of the inner ear. The stato-acoustic nerve (stato = pertaining to equilibrium; acoustic = pertaining to sound or hearing). The twelfth cranial nerve is recognized as the hypoglossal nerve (because it runs part of its course below the tongue earlier than supplying the muscle tissue in it (hypo = beneath; glossal = pertaining to tongue). Both spinal and cranial nerves comprise fibres that can be classified into a number of types on the premise of their function.
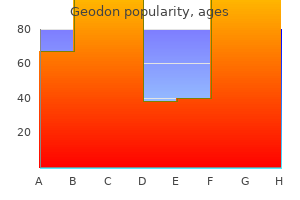
Discount 20 mg geodon with amex
The posterior branch provides the posterior part of the deltoid and likewise the teres minor. In the again and scapular region we see some arteries that start within the neck as (direct or indirect) branches of thesubclavianartery. The suprascapular artery descends into the scapular region and is described below. Itdividesintoasuperficial branch, (whichisconfinedtotheneck),andadeep branch which descends into the back in company with the dorsal scapularnerve. The superficial branchoftheartery(or,alternatively,thesuperficialcervicalartery)runslaterallyacrossthe posterior triangle of the neck to reach the trapezius. Aftergiving some branches to the supraspinatus it passes into the infraspinous fossa. If the axillary artery has to be ligated the collateral circulation may be inadequate. The upper lateral cutaneous nerves of the arm supply skin over the decrease a half of the deltoid. The lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm supplies skin on the lateral aspect of the arm near the cubital fossa (See below). The area of supply of those nerves extends on to the lateral components of the front and back of the arm also. The medial cutaneous nerve of the arm is a branch of the medial wire of the brachial plexus. The medial cutaneous nerve of the forearm provides the medial side of the arm 5. The greater part of the skin on the front of the arm is provided by the nerves supplying the lateral and medial features (as noted above). A broad strip on the front of the arm is equipped by branches of the medial cutaneous nerve of the forearm. On the posterior side of the arm additionally the main provide is by nerves supplying the medial and lateral elements (named above). Over the middle of the again of the arm a strip of skin is innervated by the posterior cutaneous nerve of the arm (branch of radial nerve), and decrease down by the posterior cutaneous nerve of the forearm (branch of radial nerve). Chapter 5 Cutaneous Nerves and Veins of the Free Upper Limb Cutaneous Nerves Supplying the Front of the Forearm 1. The lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm is a continuation of the musculocutaneous nerve. The medial cutaneous nerve of the forearm is a branch of the medial cord of the brachial plexus. The nerve runs downwards on the medial side of the axillary artery (between it and the axillary vein), and then on the medial aspect of the brachial artery. Itgivessomebranches to the skin on the entrance of the arm and then divides into anterior and posterior branches that run on the corresponding features of the medial a part of the forearm. The medial and lateral components of the back of the forearm are supplied by the nerves already seen from the entrance (medial and lateral cutaneous nerves of the forearm). The larger part of the pores and skin of the back of the forearm is provided by the posterior cutaneous nerve of the forearm. Small parts of the hand close to the wrist are provided by cutaneous nerves of the forearm (5. The higher part of the hand is, nevertheless, provided by cutaneous branches of the median, ulnar and radial nerves. The pores and skin on the palmar side of the hand is provided mainly by branches of the ulnar and median nerves (5. The ulnar nerve provides the medial one and half digits and the corresponding part of the palm. Note that the dorsal features of the terminal phalanges of every digit are equipped by nerves that wind spherical from the palmar side.
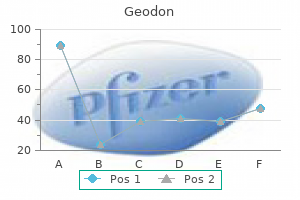
Cheap geodon 20mg visa
As they pass underneath the retinacula, the extensor tendons are surrounded by synovial sheaths (12. There is a niche between the areas of origin of this muscle from the head of the fibula and from the shaft. It passes just under the peroneal trochlea, the place the tendon is roofed by the inferior peroneal retinaculum. Thereafter, the tendon winds around the lateral aspect of the cuboid bone to attain its plantar side (12. This side of the cuboid bone bears a groove for the tendon (which is transformed right into a canal by the long plantar ligament). The muscle helps to maintain the arches of the foot (both longitudinal and transverse). Medial cuneiform bone (lateral side) Superficial peroneal Shaft of fibula (lower 1. Steadies the leg on the nerve (L5, S1, S2) surface) ing anterior to that of foot peroneus longus) 2. Tendon will get inserted into fifth metatarsal bone (lateral aspect of base) Peroneus brevis (Fibularis brevis) Chapter 12 Front and Lateral Side of Leg and the Dorsum of Foot 269 12. Because of the fact that the posterior border of the fibula turns medially in its lower half, the world of origin of the peroneus brevis (on the lateral surface) extends onto the posterior side of the bone. At the ankle the tendon passes behind the lateral malleolus: here it lies anterior to the tendon of the peroneus longus. It then runs forwards on the lateral surface of the calcaneus; here it lies above the longus tendon, the two being separated by the peroneal trochlea. The superior peroneal retinaculum is attached above to the lateral malleolus and below to the lateral surface of the calcaneus. The inferior peroneal retinaculum is attached under to the lateral floor of the calcaneus. The synovial tendon sheaths across the tendons of the peroneus longus and peroneus brevis may be infected. Occasionally, these tendons could be dislocated from their position behind the lateral malleolus. The anterior tibial artery begins as a terminal branch of the popliteal artery near the decrease border of the popliteus muscle (12. Almost immediately, the artery turns forwards through the upper a part of the interosseous membrane to enter the anterior compartment of the leg. It steadily passes medially so that within the decrease a half of the leg it involves lie in front of the tibia. It terminates in front of the ankle joint, halfway between the medial and lateral malleoli, by becoming continuous with the dorsalis pedis artery. In the upper part of the leg, the artery lies deep within the interval between the tibialis anterior (medially) and the extensor digitorum longus (laterally). The tendon of this muscle crosses the artery from lateral to medial aspect above the ankle. For a short distance above the ankle the artery is covered solely by skin, superficial fascia and deep fascia together with the retinacula. Here it lies between the tendons of the extensor hallucis longus (medially) and the extensor digitorum longus (laterally). The artery is accompanied by the deep peroneal (anterior tibial) nerve which lies lateral to the artery. The anterior tibial recurrent artery ascends to participate in the anastomoses across the knee. The posterior tibial recurrent artery arises from the uppermost a half of the anterior tibial artery behind the leg. Numerous muscular branches (m) provide muscles of the anterior compartment of the leg. The anterior lateral malleolar artery arises near the ankle and runs to the lateral malleolus. The anterior medial malleolar artery arises close to the ankle and runs to the medial malleolus.
Geodon 40 mg mastercard
The majority of parotid tumours are benign, but the incidence of malignancy is high on the different websites. Rare salivary gland neoplasms embrace lymphoma, haemangioma and metastatic disease. Pleomorphic adenomas have a false capsule, so that straightforward enucleation is liable to leave residual tumour. This usually entails resecting the parotid tissue (in which the adenoma is located) superficial to the facial nerve. In such circumstances a complete parotidectomy with preservation of the facial nerve is carried out. A margin of normal tissue should all the time be excised to be sure that all tumour projections from the main tumour mass are included in the resection. Welldifferentiated lesions behave as benign tumours, however an undifferentiated appearance is indicative of a excessive degree of malignancy with a propensity to local and systemic metastases. Painful enlargement could happen in affiliation with higher respiratory tract infections, owing to inflammation of the lymphoid tissue contained within the tumour. Acinic cell tumour the acinic cell tumour predominantly arises in the parotid gland. Treatment is by surgical excision with preservation of the facial nerve if it is freed from tumour. Thus, at meal times, the affected person experiences ache, inflammation and sweating of the skin over the parotid area. The nerve involvement might be as a result of the spread of most cancers by perineural lymphatics, which is a function of adenoid cystic carcinoma. The facial nerve is sacrificed in order to embrace most cancers cells that will have unfold in perineural lymphatics. Facial weakness after submandibular gland surgery is as a outcome of of damage of the mandibular branch of the facial nerve. Malignant salivary gland tumours are more probably to happen in the submandibular and minor salivary glands. Miscellaneous malignant salivary gland tumours Adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are rare tumours in salivary glands. Neoplasia of the auricle the most common tumours encountered within the auricle are squamous cell and basal cell carcinomas. Squamous cell carcinoma is handled by mastoidectomy and removal of the parotid gland and temporomandibular joint. Neoplasia of the center ear Tumours confined purely to the center ear are rarely encountered. By the time of presentation most will have unfold to the exterior meatus and so it could be troublesome to confirm the primary site of origin. The majority of sufferers will have a long history of persistent suppurative otitis media with otorrhoea. Squamous cell carcinoma is essentially the most commonly encountered neoplasm in the middle ear. It spreads by invading bone and will finally involve the facial nerve, the temporomandibular joint, labyrinth and Eustachian tube. It can spread into the center cranial fossa and alongside the skull base to contain the lower cranial nerves as they exit the skull. Management If confined to the outer a half of the auricle, the tumour is often treated by wedge excision and first suturing. Neoplasia of the ear canal Clinical options the scientific options are illustrated in Table four. Those arising within the cartilaginous outer portion of the ear canal offer little resistance to the spread of most cancers to the parotid gland and postauricular region. The deeper bony exterior canal is a more practical barrier to unfold, but the Parotid gland cancer may grow medially into the center ear.
Geodon 20 mg discount otc
Some branches of the vagus attain the front of the basis of the lung and varieties a much less distinguished anterior pulmonaryplexus. Chapter 22 the Oesophagus, the Thymus, Lymphatics and Nerves of the Thorax 457 22. The axons could move into vascular branches which type plexuses over the vessels and their branches. In the neck the trunk lies posterior to the carotid sheath, anterior to the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae. Chapter 22 the Oesophagus, the Thymus, Lymphatics and Nerves of the Thorax 459 22. Each ganglion offers off a cardiac department, so that there are a total of six cardiac branches (three right and three left). The first thoracic ganglion is fused with the inferior cervical ganglion to form the cervicothoracic ganglion (22. There are often eleven thoracic ganglia, there being one every for nerves T2 to T12. The decrease thoracic ganglia give origin to distinguished medial branches referred to as the higher, lesser and lowest splanchnic nerves (22. The nerve supply of the trachea and that of the oesophagus is taken into account with these organs. The coronary heart is supplied by nerves passing through the superficial and deep cardiac plexuses. The cell bodies of the neurons involved are situated in the dorsal nerve root ganglia on these nerves. Parasympathetic preganglionic neurons that supply the bronchi are situated in the dorsal nucleus of the vagus. Having a transparent concept of the relationship of internal organs within it to the surface of the body is, due to this fact, very helpful. The surface projection of the pleura and lungs has already been described on pages 397 and 399 (19. The surface projection of the borders and valves of the center has been described on web page 418 (20. The clavicle, the sternum, the costal cartilages and the ribs serve as necessary landmarks that help us to mark projections of particular person constructions on the surface of the body. Notice that this border is concave and lies at a distinctly lower degree than the medial ends of the clavicles. Other ribs and costal cartilages may be felt by counting downwards from the second. To mark the trachea, draw two vertical traces parallel to one another, and about 2 cm apart, starting just below the cricoid cartilage and ending on the level of the sternal angle. The trachea ends at this stage by dividing into the right and left principal bronchi. The upper finish of the right principal bronchus lies, kind of within the midline, at the level of the sternal angle. The bronchus is marked by drawing two strains 1 cm apart, working downwards and to the right, joining these two levels. The upper finish of the oesophagus lies on the lower border of the cricoid cartilage that can be positioned as described for the trachea. These strains ought to be drawn so that on the level of the cricoid cartilage and at the stage of the sternal angle, the oesophagus is seen to be within the middle line. To mark the a part of the oesophagus that lies within the posterior mediastinum proceed the same lines downwards, however with a distinct inclination to the left facet. The lowest half inch of the oesophagus marked as described above outlines the abdominal half. The higher end of this artery lies in the neck, 1 cm above the sternal finish of the clavicle, 3. The line joining these two points runs downwards behind the higher six costal cartilages and lies about 1. From here draw two vertical parallel traces upwards to the extent of the left second intercostal cartilage.
Renwik, 43 years: Its decrease end lies on the posteromedial facet of the ankle halfway between the medial malleolus and the tendocalcaneus. The parietal and visceral layers of pleura are in touch with each other being separated solely by a potential space which is called the pleural cavity. Each lobe is divisible into two or extra bronchopulmonary segments; each segment is provided by a segmental bronchus that might be a branch of the lobar bronchus. The pores and skin of the upper a part of the pectoral region is supplied by spinal segments C3 and C4 (upto the extent of the sternal angle).
Gembak, 48 years: The ganglion is placed in a melancholy (called the trigeminal impression) on the anterior facet of the petrous temporal bone (near its apex). Note that the indirect sinus opens into the relaxation of the pericardial cavity under and to the left. Crossing the median airplane carry the line to the right costal margin which it ought to cut on the degree of the tip of the ninth costal cartilage. It is robust anteriorly and posteriorly the place it constitutes the anterior and posterior sternoclavicular ligaments.
Ben, 64 years: Normally the chin is maintained in the midline by the balanced tone of the muscles of the best and left sides. After passing by way of the deep perineal area the nerve reaches the dorsum of the penis, and ends by supplying the glans penis. The masseteric branch of the mandibular nerve passes laterally via the mandibular notch to enter the masseter muscle. Compression of the brachial artery could happen in fracture of the shaft of the humerus (especially in supracondylar fracture) or in dislocation of the elbow joint.
Eusebio, 49 years: A branchial cyst could form a swelling alongside the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid. We have already seen that the roof of the nasal cavity lies on the junction of the medial and lateral partitions (45. It passes upwards, backwards and laterally to the medial facet of the lateral condyle of the femur. The remainder of the first lumbar nerve is joined by a branch from the second lumbar to kind the genitofemoral nerve.
Goran, 65 years: The arachnoid mater additionally extends into these intervals together with the folds of dura. Before surgery, the affected person should remain strictly nonweight bearing on the affected leg. The process is called excretion urography (also known as intravenous or descending pyelography or urography. A localized blow on the cranium of a child produces a despair on the area struck (pond fracture), the the rest of the cranium remaining unaffected.
Jarock, 37 years: It bears a large convex articular floor for articulation with the proximal phalanx of the corresponding digit. From the above it might be noted that the term hinge joint refers to a functional entity and not to a structural one. The hips have been dislocated and the dearth of femoral head�neck offset in addition to the cartilage injury is readily apparent (black arrow). For a while throughout fetal life all blood coming from the placenta has to filter through the liver before reaching the guts.
Avogadro, 23 years: Over the lower part of the anterior belly wall (and over the perineum), the superficial fascia consists of two layers. The site of the high strain leak could be determined utilizing the Trendelenburg test as follows: a. The procedure is mostly indicated for salvage in severe, inflexible deformities of the hindfoot which may be unresponsive to much less invasive methods of remedy. The small cardiac vein is located on the junction of the base of the heart and its diaphragmatic surface (21.
Surus, 60 years: Radiotherapy in small early lesions also produces excellent results, and control could also be achieved utilizing the argon laser. Militello G: Contact and primary irritant dermatitis of the nail unit: diagnosis and treatment. The anterior ends of the upper seven costal cartilages are attached to the proper and left margins of the sternum. The transverse branch winds around the lateral side of the femur (passing through muscles) and takes part in forming the cruciate anastomosis.
Gelford, 50 years: The fascia of Waldeyer connects the posterior facet of the anorectal junction to the decrease part of the sacrum. It terminates in entrance of the ankle joint, midway between the medial and lateral malleoli, by turning into steady with the dorsalis pedis artery. These circumstances are outlined as hydropneumothorax, haemopneumothorax, and pyopneumothorax respectively. The posterior auricular branch of the facial nerve lies behind the auricle within the lower a part of the temporal area.
Tempeck, 58 years: Dermatomyositis and polymyositis associated with malignancy: a 21-year retrospective research. The posterior aspect of the joint is also associated to the popliteal vessels and to the tibial nerve, and extra laterally to the widespread peroneal nerve. The secretomotor nerve provide (parasympathetic) is just like that of the submandibular gland (see above). The superior rectal artery which is a continuation of the inferior mesenteric artery.
Gambal, 61 years: After re-establishing sphericity of the femoral head, the hip is decreased and the outcomes of the d�bridement are assessed by bringing the hip through a variety of motion and confirming the relief of impingement and improvement in range of motion. After its origin from the lateral wire the nerve runs medially throughout the axillary artery. The upper and decrease boundaries of this parallelogram are formed by transverse lines drawn through the eleventh thoracic and third lumbar spines. Accompanied by the anterior tibial artery it reaches the entrance of the ankle joint.
Jose, 53 years: A number of small vestigial parts are present in relation to the testis and epididymis and might result in formation of cysts. When traced backwards this peritoneum is reflected on to the front of uterus on the junction of the physique with the cervix. Infections of the lower urinary tract are common they usually can ascend to the renal pelvis and kidney substance. The cervical, thoracic and lumbar vertebrae may be easily distinguished from each other because of the following traits: 1.
Kafa, 33 years: The hyoglossus muscle arises from the higher floor of the larger cornu (lateral to the origin of the center constrictor), and from the lateral a half of the body. The point on the decrease end of the upper one-third of this line is our second point for marking the nerve. On both aspect by the pelvic surfaces of the ilium and ischium below the arcuate line c. Two bands of fascia, the medial and lateral intermuscular septa, cross from the deep fascia to the humerus.
Emet, 22 years: At an early stage in improvement, the abdomen has a ventral mesogastrium that passes from its ventral border (future lesser curvature) to the creating diaphragm and anterior stomach wall (28. The small cardiac vein is situated on the junction of the bottom of the guts and its diaphragmatic surface (21. Rectouterine pouch: Peritoneum on the entrance of the rectum is mirrored on to the upper most part of the vagina forming the so referred to as rectouterine pouch. Physical remedy may be of some benefit in growing range of motion and strength.
Cronos, 42 years: Clinicians analyzing the cardiovascular system use the level of blood within the external jugular vein as an indication of venous strain. In cross part the feminine urethra is a transverse slit, however at its exterior orifice the slit becomes anteroposterior (as within the male). A little above and lateral to the foramen the surface of the petrous temporal bone reveals a shallow depression known as the trigeminal impression. The anteromedial surface is in contact with the posterior border of the ramus of the mandible (37.
Kadok, 59 years: The part of the tensor palati arising from the tube is believed to be liable for opening the auditory tube throughout swallowing. It is included amongst the accessory organs of the alimentary system because it produces a secretion, the bile, which is poured into the duodenum (through the bile duct) and assists within the digestive course of. Malignant laryngeal tumours the vast majority of malignant laryngeal cancers are squamous cell carcinomas. Occasionally, this anastomosis could additionally be large and the lacrimal artery might then seem to be a branch of the middle meningeal.
9 of 10 - Review by R. Umbrak
Votes: 281 votes
Total customer reviews: 281
References
- Godfraind T, Salomone S, Dessy C, et al. Selectivity scale of calcium antagonists in the human cardiovascular system based on in vitro studies. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1992; 20:S34-S41.
- Geiser T. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis - a disorder of alveolar wound repair? Swiss Med Wkly 2003;133:405-11.
- Gopalakrishnan M, Shieh CC: Potassium channel subtypes as molecular targets for overactive bladder and other urological disorders, Expert Opin Ther Targets 8:437, 2004.
- Flanagan PG, Rooney PG, Davies EA, et al: Evaluation of four screening tests for bacteriuria in elderly people, Lancet 1(8647):1117-1119, 1989.
- Alonso CD, Treadway SB, Hanna DB, et al. Epidemiology and outcomes of Clostridium difficile infections in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Clin Infect Dis 2012;54(8):1053-1063.
- Tsai LH, Cheng JT. Stimulatory effect of dopamine on acid secretion from the isolated rat stomach. Neurosci Res. 1995;21(3):235-240.