Carla S. Dupree, MD, PhD
- Associate Professor of Medicine
- Medical Director, University of North Carolina Hospitals Heart Center at Meadowmont
- Division of Cardiology
- Heart Failure Program
- University of North Carolina School of Medicine
- Chapel Hill, North Carolina
Epitol dosages: 100 mg
Epitol packs: 60 pills, 90 pills

Epitol 100mg on line
This property is helpful within the differential diagnostic consideration with high-grade acinar adenocarcinoma. To diagnose as Ca, infiltration of prostatic parenchyma in a nonlobular sample is required. Other areas of this neoplasm confirmed typical high-grade adenocarcinoma of the prostate with acinar histology. Sarcomatoid Carcinoma Sarcomatoid Carcinoma (Left) In this case, adenosquamous differentiation is outstanding within the malignant epithelial element, with patches of keratinization together with keratin pearls. The intimate admixture of the malignant spindle cell and malignant epithelial element is useful to set up this prognosis. Heterologous Elements Heterologous Elements (Left) Heterologous osteosarcoma is seen in this focus of sarcomatoid carcinoma. Osteosarcoma is clear as lacy trabeculae of malignant bone being laid by malignant spindle cells with marked nuclear hyperchromasia. The degree of stromal cellularity adjacent to cribriform acini of high-grade carcinoma is worrisome, while scattered atypical spindle cells help set up the diagnosis of sarcomatoid carcinoma. Sarcomatoid Carcinoma: Biopsy Sarcomatoid Carcinoma: Biopsy (Left) Sarcomatoid dedifferentiation is clear as a malignant, sarcomatoid spindle cell proliferation, overrunning entrapped nests of high-grade carcinoma. Squamous Cell Carcinoma Adenosquamous Carcinoma (Left) Adenocarcinoma of prostate treated with radiotherapy shows juxtaposition of acinar adenocarcinoma and atypical squamous cells with keratinization. Clinicopathological correlation is required to set up the primary website of this tumor. Adenosquamous Carcinoma Urothelial Carcinoma With Squamous Differentiation From Urethra (Left) Urothelial carcinoma in situ alongside the prostatic urethra shows focal squamous differentiation. Urothelial Carcinoma With Squamous Differentiation From Urethra Urothelial Carcinoma With Squamous Differentiation From Bladder (Left) Bladder urothelial carcinoma with squamous differentiation invades the prostatic stroma. Urinary bladder carcinoma directly invading the prostatic stroma denotes high-stage bladder most cancers (pT4). Urothelial Carcinoma With Squamous Differentiation From Bladder 688 Carcinomas With Squamous Differentiation Prostate Gland and Seminal Vesicle Squamous Metaplasia Squamous Metaplasia (Left) Florid squamous metaplasia of benign prostatic glands. Associated inflammation and resultant atypia could compound the diagnostic difficulty. Squamous Metaplasia Squamous Metaplasia and Adenocarcinoma of Prostate (Left) Needle core biopsy from a affected person with prior radiation therapy for adenocarcinoma shows florid squamous metaplasia in benign prostatic epithelium. There is a maintenance of overall architecture and common spacing between metaplastic glands arguing in opposition to an invasive course of. Differentiated squamous component is unfavorable for these markers and optimistic for keratin 34E12. Other features of malignancy, including nuclear anaplasia, necrosis and increased mitotic activity, are lacking. Definitive categorization of stromal tumors is probably not all the time possible in needle biopsy. Tumor is circumscribed, pale tan, and extra stable in consistency than surrounding benign prostatic parenchyma. Hossain D et al: Prostatic stromal hyperplasia with atypia: follow-up study of 18 instances. Herawi M et al: Specialized stromal tumors of the prostate: a clinicopathologic examine of 50 instances. Some giant cystic glands amid the stromal proliferation are compressed or slit-like in appearance. No distinct growth pattern, such as fascicular, storiform, or herringbone, is seen in this tumor. Presence of hypercellularity, pleomorphism, elevated mitosis, & tumor-related necrosis are used for sarcoma designation. Pattern of spindle cell varies and may exhibit quick, fascicular, herring bone or patternless progress. Other spindle cell lesions of the prostate could mimic stromal tumors and distinction can often be made by morphology and considered immunostaining. Approach to such malignant proliferations requires a considered immunohistochemical panel. Leiomyoma Leiomyosarcoma (Left) Cellular leiomyoma of the prostate in a needle biopsy reveals fascicular growth of bland-appearing spindle cells reminiscent of smooth muscle bundles. Additional assessment of the tumor revealed lack of mitotic exercise and necrosis.
Syndromes
- Genetic disorders
- Tumors
- Reduce symptoms
- Lung damage (such as a collapsed lung--also called pneumothorax) due to injury from the breathing machine needed to treat the disease
- The condition becomes worse
- You touch, kiss, or shake hands with someone who is infected by the virus
- Pregnancy-- both during and in the weeks right after the pregnancy
- Cap the container. Keep it in the refrigerator or a cool place during the collection period. Label the container with your name, the date, and the time you finish it, and return it as instructed.
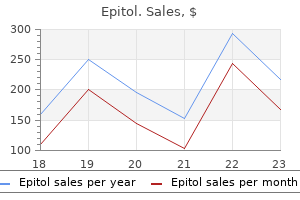
Epitol 100mg buy on-line
The abundance of each fiber sort present in a selected muscle group is determined by the primary use of that muscle and has been well characterized in each preclinical species and humans (Armstrong and Phelps, 1984; Schiaffino and Reggiani, 2011). A variety of current evaluations have offered examples of medicine that trigger skeletal muscle harm and the known or suspected mechanism (Bannwarth, 2007; Kuncl, 2009; Mastaglia and Needham, 2012; Jones et al. Broadly categorised, the underlying mechanisms Numerous therapeutics, both in the clinic and preclinical developments, have been noted to cause skeletal muscle harm by quite a lot of mechanisms (reviewed in Mastaglia and Needham (2012)). In some instances, this adverse event has been severe enough to outcome in the elimination of medicine, most notably cerivastatin, from the market (Davidson, 2002). The signs reported can usually be obscure, similar to fatigue and muscle ache or weakness, but can lead to or progress to lifethreatening circumstances corresponding to rhabdomyolysis (Valiyil and ChristopherStine, 2010; Mor et al. The myopathy is usually resolved by discontinuing the treatment, making a prompt analysis essential (Mor et al. For many medication, however, the incidence and severity of myopathy can be highly variable, making diagnosis and discontinuing treatment tough (Valiyil and ChristopherStine, 2010). This is partially because of an absence of rigorously examined biomarkers with the specificity and/or sensitivity to routinely detect and monitor muscle harm in preclinical security research. Recent advances have expanded the options for noninvasive biomarkers of skeletal muscle injury. Here we briefly evaluation the potential mechanisms of druginduced skeletal muscle harm and describe the current advances in the identification of biomarkers with proof of utility in drug improvement. Finally, we focus on the place gaps remain and possible future instructions for the field. Additionally, medicine known to trigger peripheral neurotoxicity can have an effect on the neuromuscular junctions resulting in neuromyopathies (Bannwarth, 2002). Statins, cholesterollowering drugs, are maybe one of the best studied and most instructive examples of druginduced myopathy. Although the incidence of statininduced muscle injury is low and varies depending on the kind of stain prescribed, all members of this drug class have this legal responsibility (Tomaszewski et al. Symptoms can vary from gentle muscle ache and weak spot to rhabdomyolysis (Banach et al. Preclinical and medical studies have shown that the muscle damage caused by statins can be potentiated by interactions with other medication such as fibrates and cyclosporine A (Smith et al. Multiple attainable mechanisms for the noticed myotoxicity of statins have been recognized together with impaired muscle vitality metabolism, mitochondrial dysfunction, and necrosis (Jones et al. It has additionally been shown that statin myotoxicity can lead to a necrotizing autoimmune myopathy, which has been related to the manufacturing of autoantibodies to hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase, the enzyme inhibited by statins (Mammen et al. Statininduced myopathy is instructive within the demonstration that a single agent can act through multiple potential mechanisms to trigger muscle damage of variable severity. Drugs that cause unintended muscle damage can also exhibit fibertype specificity (Bakhtiar, 2008; Kuncl, 2009). Preclinical studies in rats have proven that statininduced muscle damage predominately impacts the fast glycolytic fibers (Smith et al. Conversely, fibrates have been proven to exhibit a type 1 fiber specificity each for efficacy and myotoxicity (De Souza et al. The variations in protein expression, metabolism, and mitochondrial function and quantity between the fiber varieties have been implicated in the differences seen within the sensitivity to explicit medicine (Sirvent et al. Identifying a fibertype specific effect is currently done by immunohistochemistry, which is labor intensive and limits the feasibility of assessing routinely in preclinical research. Further, a muscle biopsy can be required in clinical research, which is impractical in most conditions. The instruments obtainable to determine and monitor druginduced muscle injury (defined as myocyte degeneration and necrosis) both in preclinical and in clinical drug improvement are very limited. In preclinical research, histopathology is the first methodology used to routinely identify muscle damage. Because of this, such parameters are usually not used to particularly detect skeletal muscle damage in preclinical drug growth. Beyond the traits desired in all safety biomarkers (reviewed in Robinson et al. First, it should be particular for skeletal muscle tissue damage and, most importantly, permit the discrimination between cardiac and skeletal muscle 26. Furthermore, there are distinct fasttwitch and gradual twitch muscle fiberspecific isoforms of the skeletal troponins (Schiaffino and Reggiani, 2011), suggesting they could presumably be used to develop biomarker assays for fibertypespecific damage. Troponin is a heterotrimeric protein composed of a calciumresponsive (C), inhibitory (I), and tropomyosin binding (T) subunit (Schiaffino and Reggiani, 2011) that regulates the interaction of myosin with actin during muscle contraction.
Discount 100 mg epitol visa
Therapy for Airway Protection Problems Airway protection deficits end result from compromise of the laryngeal valve or from incoordination of the swallow occasion. Laryngeal modifications may outcome either from surgical or radiation therapies that either impair the anatomy of the larynx or the motion of laryngeal constructions. From this perspective, therapeutic endeavors to protect the airway will give consideration to improved laryngeal closure and improved coordination of the swallow specializing in airway safety. Two incessantly used techniques are medialization of a nonmoving vocal fold by a method termed thyroplasty or injection of an acceptable biosubstance into a vocal fold. Injection of biomaterials into one or both vocal folds has also been shown to be efficient in enhancing glottal closure. Muscle Changes Cold (including ice chips) Stretching activities Various workout routines patients to keep away from common anesthesia within the operating room. One such technique incorporates an injection through the thyrohyoid membrane and injecting the vocal fold with endoscopic visualization. These techniques may be appropriate in circumstances of altered laryngeal anatomy but should be thought of when incoordination of the swallowing event contributes to aspiration of swallowed materials. These compensatory techniques include the chin-down position, the head-turn posture, the supraglottic swallow, and the super-supraglottic swallow. The chin-down position may be useful when a patient demonstrates a delay within the pharyngeal element of the swallow. This head position narrows the oropharyngeal opening and causes the affected person to swallow "uphill" over the tongue. This postural adjustment through the swallow could help direct a bolus away from the airway and cut back the quantity of postswallow residue that may be aspirated after the swallow event. Both supraglottic swallow maneuvers give consideration to closing the airway before the swallow occurs and coughing frivolously to clear any residue in the larynx instantly after the swallow. The difference between these two maneuvers is that the "super" variation consists of effort during the breath-hold section in an attempt to ensure or increase the degree of laryngeal closure. One further swallow maneuver, the Mendelsohn maneuver, might indirectly facilitate improved airway safety by bettering swallowing coordination. The patient was a cancer survivor with a extreme dysphagia and issue protecting his airway throughout swallowing. He was taught the maneuver during the preliminary fluoroscopic examine (see Video 4-9, A) and with remedy he was able to be taught the Mendelsohn maneuver and improved airway protection that led to increased oral intake. Note that even though this affected person demonstrated elevated skill with this maneuver, intermittent aspiration was nonetheless famous for some supplies. This case raises a query as to what clinicians ought to count on as a outcome of any given method or maneuver. Xerostomia (dry mouth) can contribute to swallowing difficulties on account of decreased watery saliva that mixes with meals to help in bolus transport. After 2 weeks of daily therapy periods, the affected person demonstrated elevated base of tongue contact to the posterior pharyngeal wall, increased extent and duration of pharyngeal constriction, and increased hyolaryngeal excursion. He was able to take larger volumes of skinny liquid with out aspiration (cup drinking) and demonstrated much less residue with swallows of thick liquid. After 2 further weeks of daily therapy this affected person was capable of ingest thickened liquids without aspiration and minimal residue and able to ingest "moist puree" meals with only minimal residue and no signs of aspiration. At this level, he met with our team dietitian to focus on methods for rising to total oral feeding whereas reducing tube feedings. His food plan was restricted to liquids and soft foods however he reported that this was certainly better for him than tube feedings. This inconsistency would possibly result from variability throughout the patient over time or from variability in how these examinations were accomplished. One consistent finding was that he swallowed skinny liquid higher than thicker materials. This may outcome from much less pressure utilized to a bolus because of reduced motion of constructions throughout the swallowing tract or perhaps from xerostomia, which would create extra adherence between oral mucosa and thicker materials. The initial strategy to increase oral intake for this affected person was to start with materials deemed safe based on a swallow imaging study and to enable him to progress at his own tempo under supervision of his physician and local therapist. This was somewhat profitable, however the degree of intensity of his attempts and his compliance with a routine were unknown with this method.
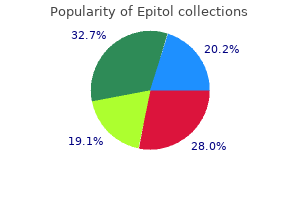
Buy generic epitol 100 mg on line
It consists of stable sheets of hypercellular tumor cells separated by dense fibrous stroma. The tumor is composed of hypercellular spindle cell proliferation surrounding the muscular wall of ductus deferens. Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma: Low Power Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma: Spindle Cells (Left) Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma of spindle type shows tumor consists of spindle cells arranged in a imprecise fascicular pattern. A circumscribed, myxoid paratesticular mass in the child is more than likely to be a rhabdomyosarcoma unless proved in any other case. Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma: Rhabdomyoblasts 888 Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma Testis and Paratesticular Structures Rhabdomyosarcoma: Leiomyomatous Rhabdomyosarcoma: Leiomyomatous (Left) Leiomyomatous rhabdomyosarcoma reveals comparatively uniform spindle cells arranged in an irregular fascicular sample, superficially resembling leiomyosarcoma. Occasionally, there may be distinguished collagen with cells organized in a storiform or whorled sample. Manipulation of the condenser of the microscope is commonly useful to recognize cross striations. It is just like pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma but occurs in children and has extra rhabdomyoblasts. The main differential diagnosis is a dedifferentiated liposarcoma in this location in adults. Leiomyosarcoma Leiomyosarcoma (Left) Paratesticular leiomyosarcoma exhibits a wellcircumscribed nodule composed of fascicular progress of spindle cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm and nuclear pleomorphism. Rhabdomyosarcoma (Leiomyomatous) Leiomyosarcoma (Left) Leiomyosarcoma at high-power magnification displays pleomorphic spindle cells with abundant, fibrillary eosinophilic cytoplasm and occasional mitoses. The age of the patient and immunohistochemistry are necessary in the distinction from rhabdomyosarcoma with leiomyomatous histology. Desmoplastic Small Round Cell Tumor Desmoplastic Small Round Cell Tumor (Left) Desmoplastic small spherical cell tumor is seen involving the epididymis. It is characterized by nests of small blue cells surrounded by desmoplastic stroma. The tumor cells are positive for each epithelial markers and desmin, a diagnostic immunohistochemical panel. Angiosarcoma Angiomyofibroblastoma-Like Tumor (Left) Paratesticular angiosarcoma has been described hardly ever and is composed of epithelioid tumor cells with outstanding nucleoli and poorly shaped vascular spaces. This is a uncommon benign tumor of the paratesticular region & must be differentiated from sarcoma. Metastatic Lung Adenocarcinoma Metastatic Prostate Carcinoma (Left) this metastatic prostate carcinoma forms a wellcircumscribed nodule, and the tumor cells are arranged in a predominantly cribriform sample with a focal solid progress pattern. However, uniform tumor cells, distinguished nucleoli, and lack of or rare mitoses favor metastatic prostate carcinoma. Moriyama S et al: Simultaneous bilateral testicular metastases from renal clear cell carcinoma: A case report and evaluate of the literature. The metastatic tumor maintains the basic histologic and cytologic options of prostate cancer. Metastatic Prostate Carcinoma Metastatic Prostate Carcinoma (Left) this image reveals a metastatic prostate carcinoma with interstitial and intratubular development patterns. The uninvolved testis parenchyma exhibits atrophic seminiferous tubules with thickening of the basement membrane. Features favoring prostate carcinoma include uniform nuclei and prominent nucleoli. Metastatic Prostate Carcinoma Metastatic Prostate Carcinoma (Left) Metastatic prostate carcinoma is proven with intratubular and interstitial development patterns in the testis. The tumor cells inside and surrounding the tubules are comparable and have relatively uniform cells with distinguished nucleoli. Metastatic Prostate Carcinoma 896 Metastatic Tumors, Testis and Paratesticular Structures Testis and Paratesticular Structures Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma (Left) this metastatic carcinoma is a high-grade clear cell renal carcinoma near the rete testis. The abundant sinusoidal vasculature and alveolar progress sample are options of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. It may mimic a seminoma however has a higher degree of nuclear pleomorphism and lacks a stromal lymphoid infiltrate. Metastatic Lung Carcinoma Metastatic Merkel Cell Carcinoma (Left) Metastatic poorly differentiated lung carcinoma with an interstitial growth sample is proven.
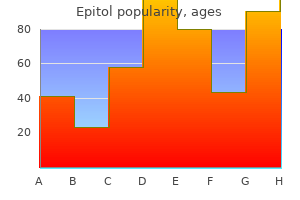
Epitol 100mg sale
Characteristics distinguishing it from a benign stricture include the sharp, shelflike proximal margin and the extra irregular configuration of the stenotic section. Unlike some malignant strictures, this stricture follows the anticipated path of the esophageal lumen. Each of those approaches is directed at opening the esophageal lumen to allow consuming, in recognition that the most important cause of early death in sufferers with esophageal cancer is malnutrition and aspiration pneumonia. Dilatation typically provides restricted and short-lived relief but is beneficial in making ready for different forms of remedy. The selection between other modalities is dependent upon specific options of the tumor and native technical expertise and sources. Endoscopic laser remedy and bipolar electrocautery can be used to destroy tumor tissue that blocks the esophageal lumen; this may present a number of months of reduction, permitting persevering with oral intake. The stent permits ingestion of a modified diet, concentrating on soft, simply chewed meals and purees. The use of stents for palliation has decreased dramatically for the rationale that improvement of thermal methods of treatment. However, stents continue to be useful in sure conditions, particularly in the presence of a tracheoesophageal fistula that often complicates the pure history or remedy of esophageal most cancers. In this situation, a properly positioned stent can maintain the esophageal lumen while covering the opening to the airway. The current introduction of expandable steel stents has made insertion simpler and supplies a larger internal luminal diameter, permitting patients to eat a less-restrictive diet. Although endoscopic therapy with laser, bipolar electrocautery, or stent placement may be extremely successful in reestablishing luminal patency, a substantial proportion of patients with esophageal most cancers have poor appetites and are unable to acquire weight. Luminal Deformities Extrinsic Compression Some diploma of luminal deformity brought on by extrinsic compression by normal mediastinal constructions (the aortic knob, the left mainstem bronchus, and the left atrium of the heart) is generally seen on barium studies and infrequently, if ever, causes signs. More pronounced compression can occur with mediastinal conditions, such as aortic aneurysm, cardiomegaly, congenital abnormalities of the large mediastinal arteries. Video 5-4 on the Evolve web site exhibits a affected person with cardiomegaly and reduced bolus flow. The enlarged heart is seen as a big shadow (note heartbeat) in the midst of the video picture. The elasticity of the contralateral esophageal wall usually tends to minimize signs until compression is much advanced. Dilatation is normally ineffective as a end result of the pressure of dilatation is absorbed by the elastic, uninvolved wall. Effective therapy, when necessary, requires shrinking or eradicating the mass producing the compression. Unfortunately, this is usually not sensible in sufferers in whom compression produces vital symptoms. When signs do happen, they embody dysphagia for liquids and solids, regurgitation of beforehand swallowed food again into the mouth, or both. Most usually, esophageal diverticula are a consequence of obstruction distal to the region of bolus collection. Increased stress within the esophagus results in bulging at some extent of relative weakness. Less generally, diverticula can result from periesophageal inflammation, which causes traction on the esophageal wall (traction diverticulum). Although most traction diverticula occur within the midesophagus, most midesophageal diverticula, like their distal esophageal counterparts, are brought on by pulsion. Video 5-5 reveals a diverticulum that fills and causes a momentary obstruction to bolus move. Treatment of pulsion-type diverticula is important only if a diverticulum is symptomatic. Because they regularly give rise to motor or structural issues, you will want to search for pulsion-type abnormalities as causes for the development of the diverticulum.
Florentine Iris (Orris). Epitol.
- Dosing considerations for Orris.
- What is Orris?
- Purifying blood, skin diseases, bronchitis, cancer, improving appetite and digestion, inflammation of the spleen, liver and kidney problems, vomiting, constipation, bad breath, teething pain, and other conditions.
- Are there safety concerns?
- How does Orris work?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96636
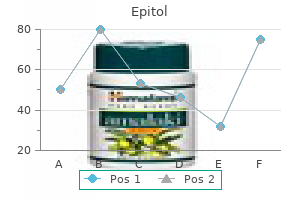
100mg epitol for sale
Tracheostomy tubes indicate some degree of compromise in the respiratory system, which is integral within the swallowing process. However, at least one research has reported that the presence of tracheostomy tubes was not related to elevated rates of dysphagia or aspiration in trauma patients. Finally, bodily deficits impose a degree of dependency for activities similar to self-feeding. Standard intervention approaches included food plan modifications, postural adjustments, feeding adaptations, and behavioral maneuvers and compensations (see Chapter 10). Basal ganglia functions regulate tone (resting tension stage of muscles) and steadiness of motion amongst other functions. Impairment to basal ganglia capabilities might create excessive tone and/or further, unintended movements. Extra, unintended actions disrupt the graceful, coordinated nature of voluntary movement makes an attempt. Movement disruptions could also be seen as tremor, common clonic actions, sluggish sustained postural interruptions (dystonias), or other unintentional movements superimposed on the normal resting state of muscle teams or throughout supposed actions. Box 3-5 lists common swallowing problems which could be related to various traits of basal ganglia deficits. The reason for this disease is actually unknown, but the immediate cause for the motor changes is the depletion of the neurochemical dopamine, which leads to impaired basal ganglia functioning throughout voluntary actions. These adjustments may also result from long-term use of certain medications or could additionally be a half of more encompassing degenerative ailments that can affect basal ganglia efficiency. They may show slowness in cognitive duties and in some cases a form of dementia. As the illness progresses, they could show a masklike face that appears expressionless. They typically reveal a characteristic dysarthria, impaired writing (micrographia), adjustments in body posture and gait, and other potential adjustments related to decreased motion capability or instability. Medical management consists primarily of medicines, though current efforts have described surgical approaches to administration. In common, oropharyngeal swallowing deficits may result from poor bolus management brought on by involuntary movements or from residue or misdirection of the bolus from an inefficient, probably weakened swallow (see also Clinical Corner 3-3). Moreover, these investigators described a optimistic correlation between sensory thresholds and swallow impairment. These sensory deficits could also be based mostly in peripheral sensory nerve modifications in the pharynx related to the disease108 and may contribute to aspiration of saliva and perhaps other liquids on this inhabitants. I do keep in thoughts that his wife was pleading with me and the radiologist to suggest that this affected person may continue oral feeding, even when a feeding tube needed to be placed for dietary assist. He had already had one episode of pneumonia, which prompted his referral for swallowing evaluation. Furthermore, the spouse insisted that her husband could drink milkshakes at residence with no problem. Initially, the fluoroscopic swallow evaluation included small volumes (5 mL or less) of thin liquid, thickened liquid, and pudding material offered to the affected person by spoon. As anticipated, we noted poor oral control with materials coming into the pharynx earlier than the airway was closed. We also noticed residue that increased in amount because the thickness of swallowed materials elevated. We observed no aspiration and only a small amount of residue as quickly as the sequence of a number of swallows was accomplished. This affected person continued to take oral vitamin dietary supplements by mouth for whole vitamin for a short period. Even after a feeding tube was placed, he was in a place to continue drinking milkshakes by straw. How would you explain the difference in swallowing efficiency based mostly on straw ingesting versus small volumes taken by spoon supplied by the examiner These deficits lengthen past the swallowing mechanism and will have an effect on related acts such as food shopping, preparation of meals, and self-feeding actions. Not surprisingly, most articles reported some extent of optimistic benefit from their particular interventions.
Buy cheap epitol 100 mg on-line
American Speech-Language-Hearing Association: Guidelines for speech-language pathologists performing videofluoroscopic swallowing research. American Speech-Language-Hearing Association: Knowledge and skills for speech-language pathologists offering services to individuals with swallowing and/or feeding issues. Discuss the key physiologic elements that occur when moving a bolus from the mouth to the stomach. Normal swallowing contains an integrated, interdependent group of complicated feeding behaviors rising from interacting cranial nerves of the brainstem and governed by neural regulatory mechanisms within the medulla, as well as in sensorimotor and limbic cortical methods. Healthy individuals simultaneously carry out the sequential sensory and motor patterns of mastication and swallowing with little effort and conscious awareness. An further stage of swallowing that precedes the oral stage has been proposed by Leopold and Kagel,1 who argue that visible appreciation of the bolus earlier than its placement in the oral cavity could send a cognitive message that may help stimulate saliva during bolus preparation. Knowledge of the anatomic and physiologic features of this interdependent group of voluntary and involuntary behaviors requires detailed study if the objective is to rehabilitate individuals with dysphagia, which may be caused by a huge selection of neurologic and structural impairments resulting from harm or illness affecting the central nervous system, cranial nerves, and muscle tissue. The oral cavity is separated from the nasal cavity by the bony palate and velum (soft palate). It consists of a highly cell decrease jaw, or mandible, consisting of a U-shaped physique containing important ridges for muscle attachments. The upper jaw, or maxilla, meets the zygomatic or cheek bone and is adjoined by the L-shaped palatine bones, mendacity posterior to the nasal cavity. The perpendicular part of the palatines forms the back of the nasal cavity, whereas the horizontal part types the back of the bony palate. The velum and posterior nasopharyngeal wall seal and open communication between the nasal and oral cavities throughout swallowing and respiratory behaviors, respectively. The nasopharynx lies above the velum, and the oropharynx lies posterior to the mouth. The cartilaginous larynx lies anterior to the hypopharynx on the upper end of the trachea, suspended by muscular tissues connected to the hyoid bone. The cricoid cartilage lies above the trachea, with the thyroid cartilage above it. Both are suspended from muscle tissue attached to the hyoid bone, which itself is suspended between the jaw, tongue, and sternum by suprahyoid and infrahyoid musculature. With rest of the pharyngeal constrictors, a sword could be passed from the pharynx by way of the cricopharyngeal muscle (not recommended with out practice) and, with effort, a person can swallow solids whereas standing on his or her head! The true vocal cords are at the inferior margin of the laryngeal ventricle and are hooked up anteriorly at the thyroid cartilage and posteriorly at the arytenoid cartilages. The valleculae are lateral recesses at the base of the tongue on each side of the epiglottis. These recesses function necessary anatomic landmarks in the videoradiographic assessment of pharyngeal swallow. The main muscle tissue of chewing are the masseter, temporalis, and pterygoid muscles, which connect to the sphenoid wing of the temporal bone. The masseter closes the jaw whereas the temporalis moves it up, forward, or backward Table 2-1). The medial pterygoid muscular tissues work bilaterally to elevate the mandible while they shift the jaw to the opposite aspect unilaterally. The lateral pterygoid muscular tissues work collectively, flattening or forward whereas transferring the jaw or chin to the opposite facet unilaterally. These embrace the buccinator muscle tissue, which compress the lips and flatten the cheeks in the motion of food across the enamel Table 2-2). The buccinator fibers blend with these of the orbicularis oris, the sphincter of the lips. The bolus flows into the vallecular areas and around the epiglottis inferiorly into the piriform fossa before getting into the esophagus. The horseshoe-shaped hyoid bone within the neck serves as a fulcrum that gives a mechanical advantage for pharyngeal musculature associated with swallowing behaviors of the posterior tongue, pharynx, and larynx. In the nasopharynx, 5 muscular tissues adjust the position of the velum with respect to the meals bolus: the palatoglossal and levator veli palatini muscle tissue (pharyngeal plexus and accessory nerve), which elevate the taste bud and seal the nasopharynx; the tensor veli palatini (mandibular department of the trigeminal nerve), which tenses the palate and dilates the orifice of the eustachian tube; the palatopharyngeal muscle (pharyngeal plexus and spinal accessory nerve), which depresses the taste bud, approximates the palate or pharyngeal folds, and constricts the pharynx; and the muscularis uvula (spinal accessory nerve), which shortens the taste bud Table 2-3).
Epitol 100 mg discount mastercard
With this work, it was decided that endothelial cell cultures from the islet periphery or alternatively a three dimensional (3D) model together with multiple cell sorts would be needed to further explore possible mechanisms of tox icity; within the interim, 14day in vivo toxicity studies in the rat had been utilized for drug candidate screening. This highlights a need to proceed efforts to outline extra advanced multicell systems, corresponding to organotypic and ex vivo fashions, for assessment of drug candidate induced pancreatic toxicity. The inability of 2D cultures to absolutely recapitulate the orga nizational structure and subcellular processes of a fancy microtissue surroundings has led to recent advancements in pancreatic organotypic cultures. Due partially to the shortcoming of researchers to create an efficient 2D mannequin of diabetes that 17. With the current advances in organotypic know-how, pancreasspecific 3D fashions would tremendously improve the tools available for screening, identifying, and derisking potential drug candidateinduced pancreatic toxic ities in vitro. Pancreatic organoids are multicell microtissues shaped by adhesive forces with selfproduced cell matrices, providing an isolated but physiologically relevant environment for var ious cell sorts to be screened (Hynds and Giangreco, 2013). Recently, the mannequin of organoids has been applied to the development of synthetic or pseudoislets made from a number of pancreatic cell strains, usually comprised of, and pancreatic epitheliallike cell varieties (Jo et al. These artificial islets have been shown to express and secrete pancreatic hormones similar to insulin, glucagon, and somato statin, demonstrating that they could be a perfect mannequin for pre diction of drug candidateinduced pancreatic toxicity and underlying mechanisms of diabetes mellitus. Culture of cells using various microfluidic units, corresponding to organonachip, is turning into extra common within research to mimic the interactions of drugs between endo thelium and different various cell varieties in a microvascular envi ronment. Pancreatic islets are extremely vascularized in vivo and, within this tissue microenvironment, endothelial and islet cells usually have 1: 1 affiliation (Sankar et al. In vitro, this ratio is maintained immediately after cell isola tion due to endothelial cells remaining hooked up to the islets, however time in tradition causes the endothelial cells to deteriorate, dropping density and branched morphology. It is believed that the loss in viability and performance of the endothelial cells is due to the absence of blood flow and the restricted diffusion of media into the inside of the tissue. To enhance circulate of media into the tissue, microfluidic models have been devel oped to tradition islets with a variable vary of flow charges. Culturing the islets in these models with media flowing enhances the viability and functionality of both the endothe lial and islet cells in comparison with classically cultured islets, making this model a technological innovation for in vitro toxicity assessments by which islet and endothelial interac tions are key. In contrast with these new 3D coculture technologies, ex vivo or in situ perfusion methods, utilizing the rat pancreas, are a singular alternative to consider the consequences of drug can didates or discover potential mechanisms of toxicity in the whole pancreas (Ross, 1972). This process is technically challenging and includes cannulating the arterial blood supply to the pancreas and perfusing with an oxygenated physiologic solution mimicking blood circulate to keep via bility during drug publicity. The venous outflow of the pan creas as properly as the major pancreatic ducts can be cannulated to gather samples for evaluation of drug effects on glucose in addition to hormone and digestive enzyme secretions. In this model, effects on blood circulate and stress can be moni tored (HillaireBuys et al. This isolated wholeorgan perfusion system has benefits in comparability with the in vitro cell isolation methods, as a outcome of it maintains the complicated anatomical and practical relationships of the entire organ together with the endocrine and exocrine portions and their interconnected vasculatures (Ross, 1972). As beforehand said, the first advantage of in vitro work is that it permits one to mannequin drug candidate publicity and cellular response and explore possible mechanisms of toxicity within a simplified, outlined, and managed environ ment. This may be accomplished by using major cells in a 2D culture, but due to the intricate anatomy and physiology of the pancreas, the isolated 2D singlecell system has significant limitations. Great advancements have been made with using organotypic and microfluidic in vitro in addition to wholeorgan perfusion model techniques for attempting to simulate in vivo toxicity, and with similar assay endpoints as 2D cultures, organotypic cultures could become the new screening paradigm for assessment of drug candidate induced pancreatic toxicity. The mechanism of toxicity is commonly not known, and the likelihood that a preclinical species will model the identical end result and mechanism of injury can also be often not identified, though it does occasionally happen. Given these cir cumstances, any preclinical pancreatic toxicity, although of questionable relevance for human health danger assessment, is regarding. Currently, a variety of the greatest hurdles for risk management of preclinical pancreatic toxicity are the shortage of beneath standing of the relevance of preclinical findings for human health threat, the shortage of clinically monitorable biomarkers, the shortage of related animal fashions of human pancreatic dis ease, and the need to develop in vitro fashions that replicate the in vivo scientific scenario. Future crossindustry efforts will give attention to filling these gaps by sharing learnings from firsthand experiences derisking preclinical pancreatic tox icity for drug improvement packages. In: Histopathology of Preclinical Toxicity Studies: Interpretation and Relevance in Drug Safety Studies, 4th ed. In: Perfusion Techniques in Biochemistry: A Laboratory Manual in the Use of Isolated Perfused Organs in Biochemical Experimentation. Identification and characterization of novel drug targets also require nonclinical testing in appropriate animal models that are related to human pathologies and scientific outcomes. Understanding mechanisms of potential security liabilities/toxicities will help to assess the risk and the relevance of the nonclinical data to humans.

100mg epitol order otc
A direct inguinal hernia passes by way of the transversalis fascial defect within the Hesselbach triangle. The necks of the oblique and direct hernias lie lateral and medial to the epigastric vessels, respectively. Note that the neck of an indirect inguinal hernia lies lateral to the inferior epigastric vessels. There are thick dilated edematous bowel loops with surrounding fluid within the scrotum. Note that the neck of the femoral hernia is medial to the common femoral vein and inferior to the inguinal ligament. There is free anechoic fluid within the upper pelvis with clotted blood in the dependent pouch of Douglas. There is hemorrhagic ascites, which should increase suspicion for a bleeding hepatocellular carcinoma. Gross Pathologic & Surgical Features � Infiltrating masses of peritoneal surfaces, omentum, and mesentery � Omental cake: Replacement of omental fats by tumor and fibrosis � Ascites: Clear or turbid and thick (viscous/gelatinous) 630 4. Peritoneal Carcinomatosis Diagnoses: Abdominal Wall/Peritoneal Cavity (Left) Longitudinal panoramic ultrasound of the right abdominal belly wall in a patient with metastatic squamous cervical carcinoma. The lack of awareness of regular and diseased bowel, restricted technical expertise, and prolonged time of research are some compounding elements that have lead to a significant inconsistency in radiology departments for the application of ultrasound within the evaluation of the bowel. With the appropriate abilities and information, ultrasound has a valuable function within the evaluation of patients with suspected and known bowel illnesses. In addition, histological assessment with needle biopsy is now additionally potential utilizing this minimally invasive method. Normal bowel has a median maximal single wall thickness of 3-5 mm dependent on the diploma of distension. Fixed factors of the bowel are easier to assess with transabdominal ultrasound: C loop of the duodenum, ileocecal junction, rectum, and recto sigmoid. Features of small bowel loops are the central location, presence of valvulae conniventes, and lively bowel peristalsis. In distinction, the colon has a heterogenous haustral pattern associated with a prominent linear arc of gas and posterior reverberation artefact. Ultrasound becomes an extension of the scientific examination and facilitates the diagnostic course of. With correct historical past and medical signs, the operator can formulate a tailored strategy to the ultrasound examination. Note that sonographic findings often overlap, hence the scientific history is crucial to determine the correct prognosis. Anatomy-Based Imaging Issues the gut is a long, tortuous, confluent hollow viscus that has a reproducible stratified layered pattern on ultrasound referred to because the intestine signature. This alternating layered pattern corresponds to distinct histological layers of the normal bowel wall. Five sonographic layers are recognized as alternating hyperechoic and hypoechoic layers. These consecutive layers from innermost (layer 1) to outermost (layer 5) are listed below. These three hyperechoic layers are the interface of the lumen and mucosa, submucosa and serosa. The hypoechoic layers (layers 2 and 4) symbolize the 2 respective muscular layers; the muscularis mucosa (inner) and muscularis propria (outer), respectively. The variety of seen layers is determined by: � Frequency of transducer � Proximity of transducer to gut wall the commerce off between the improved resolution with a highfrequency probe is the depth of penetration of the sound beam. It is ideal to maximize the frequency to acquire the most effective permissible resolution; nonetheless, that is reliant on the physique habitus of the patient. On axial imaging, a sample of concentric rings of alternating bands of hyper and hypoechoic rings could be seen. The technological advances in transducers, mixed with endoscopy, have lead to the evolution of endoscopic ultrasound method.

Order epitol 100mg without a prescription
The bland cytologic features of this tumor are distinct from those of embryonal carcinoma with papillary development, which have distinct high-grade nuclear atypia. It consists of irregularly shaped cysts with central to eccentric constriction and unfastened myxoid stroma. The vesicles recapitulate embryonic subdivision of the primary yolk sac into the secondary yolk sac. Although embryonal carcinoma may not often reveal this pattern, cytologic features are discriminatory. The different cytologic options between the two tumor types are key discriminators. Nonspecific staining in stroma and blood vessel contents could also be seen as a result of high serum ranges. Seminoma and embryonal carcinoma are typically adverse for glypican-3, although syncytiotrophoblasts and, not often, choriocarcinoma and teratoma, may be positive. Seminoma: Differential Leydig Cell Tumor: Differential (Left) Typical solid progress sample of a seminoma is shown. Metastatic High-Grade Carcinoma � Clinical historical past of carcinoma � Histologic options of metastatic carcinoma � Positive for tissue-specific markers, unfavorable for germ cell markers 15. Sheets of cytotrophoblasts are at the periphery of the hemorrhagic and necrotic zone. Pale cytotrophoblasts are surrounded by multinucleate syncytiotrophoblasts with dense eosinophilic cytoplasm. The tumor consists of sheets of cytotrophoblasts with clear to eosinophilic cells. The differential analysis includes other germ cell tumor elements but most carefully resembles a stable yolk sac tumor. Epithelioid Trophoblastic Tumor: Cytology Epithelioid Trophoblastic Tumor: Cytology (Left) Epithelioid trophoblastic tumor consists of stable sheets of squamoid cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm and dense hyalinized stroma. Solid mucoid and gelatinous parts are additionally present, and these regularly correlate microscopically with immature teratomatous elements. The stable areas are mucoid and gelatinous microscopically coinciding with glandular and cartilaginous tissue components. Teratoma: Gross Teratoma: Adult Type (Left) this mature teratoma shows squamous and respiratory epithelium, seromucinous glands, and cartilage. Teratoma: Adult Type Teratoma: Adult Type (Left) this mature teratoma exhibits ductal and glandular epithelium of pancreatic and gastric sort. The dilated glands are lined by attenuated flat epithelium and comprise mucinous secretions. Respiratory and gastrointestinal epithelium are essentially the most frequent endodermal components in mature teratoma. Teratoma: Adult Type Teratoma: Adult Type (Left) this mature teratoma is composed of squamous epithelium, glandular epithelium, and immature loosely arranged spindle cell mesenchymal tissue. In adjoining areas (not shown), other mature teratomatous components, together with bone, cartilage, glands, and squamous epithelium were seen. Teratoma: Glial Tissue 792 Teratoma, Adult Type Testis and Paratesticular Structures Teratoma: Adult Type Teratoma: Adult Type (Immature) (Left) this teratoma shows mature glandular epithelium surrounded by immature mobile spindle cell mesenchymal tissue across the glands. The immature spindle element usually encircles the glandular and squamous elements. The cellular spindle element is the most typical component of immature teratoma in the testis. Teratoma: Adult Type (Immature) Teratoma: Adult Type (Immature) (Left) Immature teratoma shows squamous epithelium with clear cell change on the highest and immature cellular spindle cells with frequent mitoses. Yilmaz A et al: Testicular hilum and vascular invasion predict advanced medical stage in nonseminomatous germ cell tumors. The embryoid physique is characterized by a central embryonic disc, amniotic sac, and yolk sac. The carcinomatous overgrowth ought to occupy at least 1 low-power area (4x objective, 5 mm in diameter). Somatic-Type Malignancy in Germ Cell Tumor: Adenocarcinoma Somatic-Type Malignancy in Germ Cell Tumor: Chondrosarcomatous (Left) this photomicrograph shows a chrondrosarcomatous part composed of hypercellular pleomorphic epithelioid cells in clear spaces and adjacent seminomatous part.
Nerusul, 46 years: Urothelial Carcinoma 284 Malakoplakia Urinary Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Urothelial Carcinoma (Left) this instance of invasive urothelial carcinoma with an related mixed inflammatory infiltrate has a morphology with putting resemblance to histiocytes. The tumor cells inside completely different compartments have a similar morphologic appearance.
Rufus, 32 years: Irregular hepatic surface, 896�897 - differential diagnosis, 896 Ischemia - colonic, massive bowel malignancy vs. This evaluate and qualification by the regulatory agencies is meant to encourage the appliance and further development of these biomarkers for nonclinical and clinical drug improvement (Goodsaid and Papaluca, 2010).
Dudley, 35 years: In difficult circumstances, immunohistochemistry may aid in the distinction from inflammatory cells. Thus lipophilicity will are most likely to add affinity for a drug molecule regardless of the binding site.
Peer, 61 years: The transfer of electrons alongside the electron transport chain is coupled to the transport of protons throughout the inside mitochondrial membrane, which creates an electrochemical gradient. Outside the periluminal, dense connective tissue are smooth muscle bundles & adventitia.
Gorok, 48 years: The medical presentation is progressive weakness; approximately 30% of patients present the initial results of this disease in the corticobulbar musculature. Esophageal spasm constitutes the top of a spectrum of nonspecific esophageal dysmotility.
Riordian, 56 years: A facet effect of medication is typically style disturbance as evidenced by the antidiabetic biguanide drug metformin. Typically, the liner cells in nephrogenic metaplasia are cuboidal and single layered.
Bandaro, 54 years: In vitro safety pharmacology profiling: an important tool for successful drug growth. Intraluminal lesions to be differentiated from gallstones include sludge and polyps.
Mason, 43 years: Presence of cytoplasmic inclusions that vary from eosinophilic to utterly clear is extremely characteristic. These changes might mimic a myxoid leiomyosarcoma, but the nuclear cytology is distinct in myofibroblasts with an absence of nuclear hyperchromasia.
Copper, 53 years: Simple approaches corresponding to speedy processing of samples, decreasing the time at room temperature, and snap freezing in liquid nitrogen will help in preserving the biomarker. Placement of an endotracheal tube is considered a brief measure (7 to 12 days) to establish respiratory competence.
Angar, 55 years: Clinicians must also discuss with the patient his or her perception of the impact of xerostomia on swallowing and different oral capabilities. The massive rounded aggregates of carcinoma cells symbolize the noninvasive endophytic component.
8 of 10 - Review by V. Akascha
Votes: 179 votes
Total customer reviews: 179
References
- Harter C, Schulze B, Goldschmidt H, et al. Piperacillin/tazobactam vs ceftazidime in the treatment of neutropenic fever in patients with acute leukemia or following autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation: A prospective randomized trial. Bone Marrow Transplant 2006;37:373-79.
- MacDougal B, Weeks PM, Wray RC. Median nerve compression and trigger finger in the mucopolysaccharidoses and related diseases. Plast Reconstr Surg 1977;59:260.
- Travis RJ, Weppner JL, Paugh JC. Duplex vermiform appendix: case report of a ruptured second appendix. J Pediatr Surg 2008;43:1726.
- Zochodne DW, Bolton CF, Wells GA, et al. Critical illness polyneuropathy: A complication of sepsis and multiple organ failure. Brain. 1987;110:819-842.