Linda M Smith-Resar, M.D.
- Professor of Medicine

https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/profiles/results/directory/profile/0004790/linda-smith-resar
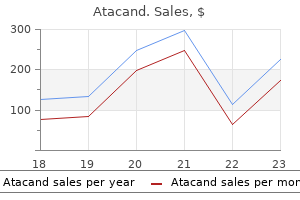
Atacand dosages: 16 mg, 8 mg, 4 mg
Atacand packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills

Atacand 8 mg safe
It is frequent within the tissue engineering literature to discover a hypothetical graph by which a hypothetical mechanical parameter is plotted versus time with three curves: scaffold, new tissue, and web assemble (or combined). The scaffold curve slopes downward with time whereas the new tissue formation curve will increase. Usually these curves are matched so that the online degree of the mechanical parameter is maintained through the healing process. Of course, in reality that is typically not the case; scaffolds remain longer than needed and potentially stress protect the tissue. This is a critical concern in that such mechanical failures lead to morbidity and mortality which have restricted the broader adoption of many degradable scaffold approaches, as indicated earlier. Also, such mechanical failure may be associated to the underlying disease process within the handled population that is most likely not obvious in preclinical testing or in the utility of such an method in different populations. Therefore, in addition to deciding on biomaterial scaffold designs with applicable preliminary mechanical parameters approximating the host tissue, matching the degradation price of temporary scaffolds to tissue integration and maturation is significantly essential. In reality, subtle models in search of to seize the underlying physics and biology are beneath improvement [12]. At a mobile scale, quite so much of analysis in has examined how the microscale mechanical properties of biomaterial scaffolds can modulate cell habits. Biomaterial substrate stiffness impacts stem cell differentiation, including mesenchymal stem cells, induced pluripotent stem cells, and embryonic stem cells [13e15]. In addition to stem cell results, substrate stiffness has been proven to affect primary cell phenotypes, including the macrophage and its polarization [18,19]. Macrophages are important cells concerned within the foreign body response; thus, substrate stiffness additionally pertains to the host tissue response to scaffolds. Researchers have proven that biomaterial stiffness modulates the adhesion, migration, and proliferation for other kinds of cells, as well [20]. Given the mechanical help functions which are outlined for a specific scientific utility of a scaffold, along with the increasingly appreciated impact that mechanical parameters can have on host response and cell behavior, choosing materials with suitable mechanical parameters is often step one in scaffold design. In comparison, artificial polymeric materials and naturally derived materials are often weaker in all main features. The blue line indicates mechanical assist by degrading scaffold; the red line, mechanical help by integrated tissue; and the green line, mixed mechanical help by the scaffoldetissue mixture. Degradation Profile As noted previously, scaffold degradation is necessary for tissue integration and ought to be well-synchronized with the latter to preserve mechanical help in implantation websites. Aside from tissue integration, degradation can have a crucial role in offering pathways for metabolite diffusion and angiogenesis, as properly as the discharge of brokers loaded into the fabric. Degradation Mechanisms the mechanisms at work in biomaterial scaffold degradation range by material kind. Enzymatic facilitation of such cleavage reactions could be an essential think about accelerating degradation in vivo, and the utilization of enzymes in degradation buffer options to research degradation in vitro is widespread. Polymer chains can also be cleaved by free radicals, irradiation, reduction reactions, and other reagents or stimulus, relying on the bonding mechanism [24e26]. Newer concepts in polymeric biomaterial degradation include elevated solubility induced by side chain cleavage [27], self-immolating depolymerization [28], and the dissociation of supramolecular assemblies [29]. Metallic biomaterials are almost exclusively selected for his or her degradation (corrosion) resistance. However, quite a lot of research has been focused on degradable metals corresponding to magnesium and zinc alloys for use as temporary scaffolds in a broad variety of applications [30e32]. The degradation of generally used ceramic scaffolds (tricalcium phosphate, hydroxyapatite, and dicalcium phosphate) begins with the dissolution of CaP components, which is heavily affected by the solubility of the particular material. Various cell types (monocytes/macrophages, fibroblasts, and osteoblasts) are then involved in the degradation process by phagocytic mechanisms or by way of an acidic mechanism to reduce the microenvironmental pH that leads to demineralization of the ceramic matrix and resorption [34]. For biologically sourced materials, particular enzymatic degradation has an essential function in degradation, and resistance to such degradation varies with the fabric composition, processing history and local tissue circumstances. Factors That Affect Degradation Rates Several factors affect the degradation charges of biomaterial scaffolds, and these elements can be leveraged to modulate the degradation profiles of corresponding scaffolds. Most clearly, the molecular composition of the scaffold will dictate the degradation profile.
Atacand 8 mg order without prescription
Starting with a patient-specific pluripotent cell affords the potential of correcting or enhancing these populations before differentiation. These thrilling advances in cell and molecular biology have nice promise in patient-specific regenerative medication. The mixture of these novel applied sciences with parallel advances in cell remedy and tissue engineering has the potential to have a meaningful influence for patients in need. The use of biological scaffolds can further help these cells in creating lung tissue ex vivo by providing a platform to enhance regeneration in an anatomically right surroundings. The choice of biomaterial and the strategies used to create these lung scaffolds are important issues that are integral to the ultimate operate of the regenerated tissue. In one study, fetal rat lung cells had been mixed with Gelfoam and injected into regular wholesome lung parenchyma; they confirmed cell survival for 35 days and supplied a supportive surroundings for recipient-derived cells to engraft [56]. Scaffolds can also be used to sequester cell-derived growth components for focused supply. The relatively simple tissue, which consists of a hollow tube with compatible mechanical properties, appears a promising first aim towards patient-specific regenerative medication. The minimal necessities for any biomaterial used for this function could be biocompatibility to the recipient and suitability as a substrate for cell attachment and survival [57]. A large variety of biocompatible supplies have been examined for this objective, together with biodegradable polymers (polyglycolic acid, polylactic acid, and polycaprolactone), and hydrogels (Pluronic F-127 and collagen gel). Important progress has been made using the nanocomposite biomaterial polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane poly(carbonate-urea) urethane. This material has been shown to be biostable, to have favorable mechanical properties, and to help the expansion of assorted cell sorts, including human bronchial epithelial cells [58]. In addition to artificial materials, decellularized native tracheas are promising scaffolds for airway engineering. Decellularized tissue engineered tracheas have been investigated in a selection of studies utilizing various species, with mixed results [59]. Although good epithelialization was noticed in plenty of reports, grafts have been structurally unstable, resulting in airway obstruction and subsequent collapse. An important consideration for large airway engineering is the long-term maintenance of biomechanical integrity and lumen patency, to forestall the necessity for subsequent dilatation or stenting of the implanted graft. When aiming to create extra complex tissues corresponding to functional lung parenchyma, the ability to create a suitable scaffold with enough tissue structure and resolution presents vital challenges. Many of these are products derived from the dermis, pericardium, small intestinal submucosa, and urinary bladder of bovine and porcine sources. Building on this idea and stemming from a seminal article on whole-heart regeneration [61], this method was first utilized to whole lungs in an thrilling collection of reports in 2010 [62e64]. Detergents used embrace sodium dodecyl sulfate, sodium deoxycholate, and 3-([3cholamidopropyl] dimethylammonio)-1-propanesulfonate. Lung decellularization has been upscaled and applied across many species together with mice [68], rats [69], pigs [66], nonhuman primates [70], and humans [66,71]. It has been confirmed that the acellular scaffolds retain important collagens, laminin, elastin, and glycosaminoglycan to help cell reattachment [66,72]. These research provide necessary perception into the composition of the bioactive scaffold upon which new tissue shall be created. If important proteins are lost through the decellularization process, or if immunogenic proteins are retained inside the matrix, there could be significant penalties for the regeneration course of both during ex vivo recellularization and after in vivo implantation [74]. Further refinement of these techniques, as applied to various biological scaffolds, will present more precise information about the connection between protein composition and total tissue regeneration and performance. The supply of native lung tissue used to prepare scaffolds can have a direct influence on subsequent regeneration. The age of the lung can contribute necessary differences to the decellularized scaffold. The capacity to management age, measurement, and any variation in environmental publicity or potential pathology would standardize the beginning material for medical lung tissue regeneration. One widely explored possibility is the porcine lung, as a outcome of pig organs are anatomically just like human organs. One examine evaluating decellularized scaffolds from rat, pig, primate, and human lungs found that human and primate lungs have been stiffer, contained more elastin, and retained fewer glycosaminoglycans than did pig or rat lung scaffolds [82]. Adhesion of human endothelial cells in the vascular network of the lung scaffold was also markedly enhanced in human and primate tissues compared with porcine and rat matrices. There are also anatomic and morphologic variations between human and porcine lungs [83].
Buy 8mg atacand fast delivery
Vitalisation of tubular coral scaffolds with cell sheets for regeneration of lengthy bones: a preliminary study in nude mice. Basic fibroblast development factor enhances osteogenic and chondrogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in coral scaffold constructs. Hydroxyapatite reinforced poly-ethylene - a mechanically appropriate implant materials for bone substitute. Bone regeneration in a canine cranial mannequin utilizing allogeneic adipose derived stem cells and coral scaffold. Miscibility and in vitro osteo-compatibility of biodegradable blends of poly[(ethyl alanato) (p-phenyl phenoxy)phospha-zene] and poly(lactic acid-glycolic acid). Nanofiber scaffolds with gradations in mineral content for mimicking the tendon-to-bone insertion website. Photografting of poly(hydroxylethyl acrylate) onto porous polyurethane scaffolds to enhance their endothelial cell compatibility. Collagen-calcium phosphate cement scaffolds seeded with umbilical cord stem cells for bone tissue engineering. Poly(L-lactic acid)/hydroxyapatite nanocylinders as nanofibrous structure for bone tissue engineering scaffolds. Osteoblast progress and bone-healing response to three-dimensional poly(-caprolactone fumarate) scaffolds. Hypoxia-mimicking mesoporous bioactive glass scaffolds with controllable cobalt ion release for bone tissue engineering. Fabrication and properties of porous scaffold of magnesium phosphate/polycaprolactone biocomposite for bone tissue engineering. Fabrication of multilayer ZrO-biphasic calcium phosphate-poly-caprolactone unidirectional channeled scaffold for bone tissue formation. Application of K/Sr co-doped calcium polyphosphate bioceramic as scaffolds for bone substitutes. Titania-hydroxyapatite nanocomposite coatings help human mesenchymal stem cells osteogenic differentiation. Porous ceramic titanium dioxide scaffolds promote bone formation in rabbit peri-implant cortical defect model. Cells of the innate immune system are sometimes the first responders to reach a web site of injury. One of their main capabilities is to comprise locally and remove, if possible, any doubtlessly harmful substances, which are commonly termed pathogens. In addition, numerous innate immune cells operate to gather small items of the damaging substance, termed antigens, and current them to cells of the adaptive immune system. Th1 immune responses induce cell-mediated responses, usually scary T-cell proliferation and investigation of intracellular pathogens. Alternatively, Th2 immune response induce humoral immunity, promoting B-cell antibody production focusing on primarily extracellular pathogens. Although tremendously simplified, this is considered one of the main processes that the immune system uses any time it encounters potentially harmful substances, whether or not that be a virus, bacteria, or most cancers cell. Cancer presents quite so much of challenges for the immune system as evidenced by the truth that avoidance of immune destruction has been acknowledged as a primary hallmark of most cancers [1]. However, most cancers has long been acknowledged as a disease mediated by genomic mutations, whether naturally or virally induced, and if these genomic mutations end in mutated proteins, the immune system theoretically has the potential to recognize that. As proof of this, tumors with a better mutational burden are usually extra immunologically lively, with higher immune cell infiltrate and a higher potential for immunemediated assault [2]. In addition to mutated antigens, differential expression of self-antigens provides one other mechanism of immunologic recognition of cancer. Another problem that hinders immune recognition and destruction of most cancers is the highly immunosuppressive protumor microenvironment observed in solid tumors. In mild of these obstacles, cancer immunotherapeutic methods are warranted to direct and stimulate an efficient immune response against cancer. Significant immunotherapy achievements embody the development of the primary immune adjuvants [5], proposal of the immune surveillance concept or the concept that most cancers cells could be acknowledged and killed by elements of the immune system [6], proof that tumors have tumor-specific antigens that can be targeted by the immune system [7e10], and proof of tumoral immune escape through the lack of tumor-specific antigens [11]. Each of those discoveries and countless extra had been monumental in the improvement of the sector of most cancers immunotherapy.
Atacand 8 mg discount otc
Clinically established hemostatic scaffold (tissue fleece) as biomatrix in tissue- and organ-engineering research. Cardiac tissue engineering: cell seeding, cultivation parameters and tissue construct characterization. Cardiac muscle tissue engineering: toward an in vitro mannequin for electrophysiological studies. Tissue engineering of functional cardiac muscle: molecular, structural and electrophysiological studies. Engineering hybrid polymer-protein super-aligned nanofibers via rotary jet spinning. A 3D aligned microfibrous myocardial tissue assemble cultured under transient perfusion. Biomimetic approach to cardiac tissue engineering: oxygen carriers and channeled scaffolds. Engineered hybrid cardiac patches with multifunctional electronics for online monitoring and regulation of tissue function. Myocardial tissue engineering with cells derived from human-induced pluripotent stem cells and a native-like, high-resolution, 3-dimensionally printed scaffold. Patterning human stem cells and endothelial cells with laser printing for cardiac regeneration. Polyurethane movies seeded with embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes to be used in cardiac tissue engineering functions. Spatially organized layers of cardiomyocytes on biodegradable polyurethane films for myocardial restore. In vitro generation of differentiated cardiac myofibers on micropatterned laminin surfaces. Novel micropatterned cardiac cell cultures with sensible ventricular microstructure. Mesoscopic hydrogel molding to management the 3D geometry of bioartificial muscle tissues. Nanoscale cues regulate the construction and function of macroscopic cardiac tissue constructs. Biowire: a platform for maturation of human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Microfabricated perfusable cardiac biowire: a platform that mimics native cardiac bundle. Recapitulating maladaptive, multiscale reworking of failing myocardium on a chip. Modeling the mitochondrial cardiomyopathy of Barth syndrome with induced pluripotent stem cell and heart-on-chip applied sciences. Defined engineered human myocardium with advanced maturation for functions in coronary heart failure modelling and restore. Engineered cardiac organoid chambers: towards a useful biological model ventricle. Optimizing cell seeding and retention in a three-dimensional bioengineered cardiac ventricle: the two-stage cellularization model. Mathematical mannequin of oxygen distribution in engineered cardiac tissue with parallel channel array perfused with tradition medium containing oxygen carriers. Pulsatile perfusion and cardiomyocyte viability in a strong three-dimensional matrix. A novel perfusion bioreactor offering a homogenous milieu for tissue regeneration. Cyclic mechanical stretch induces cardiomyocyte orientation and polarization of the hole junction protein Connexin43. Biphasic electrical field stimulation aids in tissue engineering of multicell-type cardiac organoids. Cell culture chips for simultaneous utility of topographical and electrical cues improve phenotype of cardiomyocytes. Electrical stimulation directs engineered cardiac tissue to an age-matched native phenotype.
Diseases
- Konigsmark Knox Hussels syndrome
- Tetraamelia ectodermal dysplasia
- Wheat hypersensitivity
- Beta-sarcoglycanopathy
- Olivopontocerebellar atrophy type 2
- Palsy cerebral
- Skandaitis
- Macias Flores Garcia Cruz Rivera syndrome
- Singh Chhaparwal Dhanda syndrome
- Peripheral type neurofibromatosis
Order atacand 16mg free shipping
Self-assembled collagen-like-peptide implants as alternate options to human donor corneal transplantation. Multi-hierarchical self-assembly of a collagen mimetic peptide from triple helix to nanofibre and hydrogel. Biocompatibility of helicoidal multilamellar arginine-glycine-aspartic acid-functionalized silk biomaterials in a rabbit corneal model. Functional innervation in tissue engineered fashions for in vitro study and testing purposes. Innervated human corneal equivalents as in vitro models for nerve-target cell interactions. Use of a silk fibroin-chitosan scaffold to construct a tissue-engineered corneal stroma. Controlled launch of acyclovir via bioengineered corneal implants with silica nanoparticle carriers. Collagen-based artificial corneal scaffold with anti-infective functionality for prevention of perioperative bacterial infections. Coloured cornea replacements with anti-infective properties: expanding the protected use of silver nanoparticles in regenerative medicine. It conducts numerous extremely complicated and numerous capabilities that are regulated by distinct cellular and useful differences along the tract size, which allow it to provide the physique with vitamins, water, and electrolytes. In addition to this, an essential symbiotic relationship exists between bacterial species that colonize the alimentary tract of the host [1]. Therefore, the surface of the alimentary tract must also present a barrier against undesirable entry of organisms and toxins. If the barrier perform is breached, specialized cells and tissues inside the gut wall provide an important part of the immune system to defend the host. Dysfunction of the alimentary tract may result from a variety of congenital and acquired conditions that can affect any of its physiological features. This article will talk about knowledge relating to tissue engineering different regions of the alimentary tract, highlighting profitable strategies in addition to failures and a few obstacles which have yet to be overcome on this quickly evolving subject. It functions primarily as a conduit to connect the pharynx with the stomach, offering coordinated peristaltic contractions in response to swallowing to propel meals into the stomach. The esophageal mucosa is lined by stratified, squamous, nonkeratinized epithelium. The submucosa accommodates muscle, nerve, blood vessels, lymphatics, and mucosal glands. The muscularis has two layers consisting of an outer longitudinal layer and an internal round layer. Both layers include striated muscle in the higher portion and smooth muscle within the decrease third, steady with the muscle layers of the abdomen. The esophagus has no serosa and its vascular provide is much less in depth in contrast with the intraabdominal parts of the intestine. Sphincters on the higher and decrease ends of the esophagus guarantee food is transferred appropriately between it and the pharynx or abdomen. The upper esophageal sphincter, found in the higher 3e4 cm of the esophagus, and the decrease esophageal sphincter, positioned 2e5 cm above the gastroesophageal junction, remain tonically and strongly constricted to prevent air from entering the esophagus throughout respiration between swallowing and reflux of abdomen contents into the esophagus between peristaltic waves, respectively. Regenerative medicine techniques are being explored for a quantity of situations affecting the esophagus. Gastroesophageal reflux illness is likely certainly one of the most common problems affecting the gastrointestinal tract, resulting from lower esophageal sphincter incompetence. Medical remedy is mostly protected and efficient generally, but for sufferers for whom this feature fails, antireflux surgery or endoscopic procedures that involve injecting bulking materials could additionally be used in an try and slender the lumen of the decrease esophagus. Attempts have been made to restore physiological function of the esophagus using regenerative drugs. Muscle precursor cells isolated from expanded satellite tv for pc cells derived from skeletal muscle fibres had been injected into the gastroesophageal junction after cryoinjury. Histology confirmed an increase in myofibers at the website of injection that had fused into newly formed or preexisting myofibers. The need remains to reveal that cells injected on this manner can contribute to functional improvement of broken esophageal sphincter, but the feasibility of utilizing this strategy provides a promising therapy for this widespread condition. Esophageal reconstruction is a requirement for congenital esophageal atresia, burns, malignancy, or severe benign illness.
Atacand 16mg purchase with mastercard
Using a culture system that mimics the native intestinal epithelial stem cell niche, these cells are capable of producing "organoids" that include all four epithelial cell forms of the small intestinal epithelium. The submucosa consists of fibrous connective tissue that provides blood and lymphatic vessels to the mucosa. The muscularis propria consists of an inside layer of circular muscle and an outer longitudinal muscle layer. The muscularis propria is roofed by the adventitia, a layer of loose connective tissue, and the serosa, a mesothelial lining of peritoneum. Intestinal ischemia and bowel resection for tumors and inflammatory bowel illness may find yourself in short bowel syndrome when greater than 75% of the small intestine is lost. Short bowel syndrome is often associated with intestinal failure and the requirement of lifelong dietary help (total parenteral nutrition), which is frequently accompanied by extreme complications similar to liver failure, line sepsis, and poor long-term survival charges. The length of residual gut is crucial for these sufferers; thus, methods for growing absorptive surface area have been sought for many years. Surgical choices for rising the absorptive surface or slowing the transit time to enhance absorption have been reported, however these approaches require longer residual intestinal segments and most have only restricted long-term clinical success [54e57]. Small bowel transplantation is a viable choice for some patients, however this process has limitations together with the supply of donor tissue, the necessity for long-term immunosuppression, graft versus host illness, and potential posttransplant lymphoproliferative dysfunction [58]. Therefore, small bowel elongation of just some centimeters might allow many patients to turn out to be unbiased of complete parenteral vitamin. Distraction enterogenesis has been devised as a novel method to increase intestinal length by making use of linearly directed pressure, resulting in increased floor space and epithelial cell proliferation [59,60]. Devices used for distraction enterogenesis embrace extralumenal, radially selfexpanding form reminiscence polymer cylinders [61]; biodegradable springs composed of polycaprolactone created to lengthen intestinal segments mechanically whereas avoiding the need for subsequent retrieval [62]; and doubleballoon catheter gadgets [63]. The use of growth factoreembedded scaffold materials is an efficient technique for improving the quick half-lives of progress elements. Local supply of the trophic growth factor improved construction of the tissue engineered intestine. Early attempts to patch bowel defects utilizing the serosal surface of another piece of gut resulted in its being lined with regenerated mucosa [68,69]. This paved the way for different researchers to investigate a wide selection of scaffold supplies, corresponding to polytetrafluoroethylene tubing, for the ingrowth of neointestine through guided tissue regeneration [70]. The use of nonresorbable materials for learning intestinal morphogenesis and regeneration continues to be interesting [71], but the use of resorbable scaffold biomaterials for intestinal tissue engineering has turn into the predominant approach. Histological evaluation confirmed the presence of mucosa, various amounts of smooth muscle, sheets of collagen, and an outer serosal layer. Similar limitations with the mechanical integrity of the scaffold materials had been reported by Pahari and colleagues, who used guided tissue regeneration to create a section of recent gut in rats using acellular dermal matrix (AlloDerm) rolled into tubes [73]. Other approaches utilizing biologically derived scaffolds included the use of allogenic aortic graft segments interposed in an excluded small bowel segment wrapped in omentum, which resulted in intestinal-like wall transformation of the aortic graft [76]. In an attempt to keep an open lumen within the tissue engineered intestine, Hori and colleagues reported that scaffolds composed of sheets of acellular collagen sponge wrapped on a temporary silicone stent and lined with omentum guided tissue regeneration of almost all layers of the gastrointestinal tract in a canine mannequin, but solely a thin muscularis mucosa was present and the muscularis propria was absent [77]. The same group explored the addition of mesenchymal stem cells seeded onto a collagen scaffold, which it was hypothesized may differentiate "site-specifically" into muscle cells and regenerate the muscle layer [78]. Intestinal regeneration occurred but muscle regeneration in an organized method was not noticed. The silicone stent was left in place for 3 weeks to keep lumenal patency throughout tissue regeneration. At 4 weeks, an epithelial layer had begun to type and fully covered the lumenal floor by 12 weeks. The neomucosa had a typical morphology containing goblet cells, Paneth cells, enterocytes, and enteroendocrine cells. Although the regenerated bowel contained bundles of clean muscle-like cells, especially close to the sites of anastomosis, the amount and group of the muscle layer differed from those found in native small intestine; they had been predominantly circular muscle with no longitudinal muscle. The use of a ThiryVella loop within the mannequin created by Wang might have facilitated mucosal growth in the neointestine by defending it from alimentary transit and creating an isolated surroundings that prevented the meals stream and digestive enzymes. Many of the studies reporting intestinal tissue engineering strategies are based on methodologies used in the pioneering work conducted by Vacanti and colleagues within the 1980s and 1990s that mixed intestinal tissue with scaffolds [81]. Important to these research were previous investigations by Tait and colleagues that showed intestinal tissue could be separated by enzymatic digestion to produce organoid models [82].
Generic 8mg atacand fast delivery
An instance is poly(butylene succinate), which is synthesized from 1,4-butanediole and succinic acid [186] and which has been evaluated for use in the regeneration of cartilage [187] and bone tissue [188]. The use of triethylene glycol because the diol component produced predominantly hydrophilic polymers, whereas hydrophobic supplies could probably be obtained through the use of 1,10-decanediol. Orthoester is a functional group containing three alkoxy teams hooked up to one carbon atom. It is thought that supplies built from functional teams with short hydrolysis half-lives and low water diffusivity tend to be surface eroding. Polymers that exhibit floor erosion can be utilized to fabricate drug delivery methods that release loaded drugs at a constant price at a high side to quantity ratio. The degradation of most polycarbonates is managed by hydrolysis of the carbonate group, which yields two alcohols and carbon dioxide, which alleviates the problem of acid bursting seen in polyesters [104,194]. The structural variation in the pendant facet groups permits polymers to be ready with completely different mechanical properties, degradation charges, and cellular responses. Altered material properties resulting from these functionalities widen the prospect for using polycarbonates in tissue and bone regeneration [196,197] in addition to in drug delivery [198,199] and as polymer-based antibiotics [200,201]. Tyrosine-based polycarbonates that include a pendant ethyl ester group have been proven to be osteoconductive and to possess mechanical properties adequate for load-bearing bone fixation. Long-term (48-week) in vivo degradation kinetics and host bone response to tyrosine-derived polycarbonates had been investigated using a canine bone chamber mannequin [205]. Variations within the composition of these terpolymers can be used to engineer ultrafast degrading and resorbing polymers that might be suitable for the coating of implants in mind tissue to minimalize antagonistic results [208]. In vivo investigations showed that each one take a look at polymers exhibited favorable tissue compatibility and degraded considerably over 1 12 months [212]. Polyurethane-urea matrices had been proven to enable vascularization and tissue infiltration in vivo [213]. To speed up the degradation habits of polyesterurethanes, polyester segments within the polymer spine have been partially substituted with polycarbonate, yielding poly(ester carbonate)urethane-ureas [215]. For controlling the response of a organic system to supplies, surface and bulk modifications are a typical technique. To this finish, a collection of biodegradable polyesterurethane-urea elastomers with variable amino content material had been developed. Via the amine teams, carboxylated phosphorylcholine was conjugated to polymer for bulk functionalization [217]. This modification significantly reduced platelet adhesion to the fabric and inhibited rat vascular easy muscle cell proliferation. Such supplies could find use as coatings in cardiovascular devices or as scaffolds for cardiovascular tissue regeneration. Amino AcideDerived Polymers, Poly(amino Acids), and Peptides Amino acids are an attention-grabbing constructing block for polymers due to the biocompatibility of the degradation merchandise and the degradability of the amide or ester bonds by which amino acids are usually polymerized or integrated in copolymers. To improve these unfavorable properties, amino acids have been used as monomeric constructing blocks in polymers that have a spine structure completely different from that of pure peptides. Based on polymer structure and chemistry, 4 main teams have been used to classify such "nonpeptide amino acidebased polymers": (1) artificial polymers with amino acid aspect chains, (2) copolymers of pure amino acids and noneamino acid monomers, (3) block copolymers containing peptide or poly(amino acid) blocks, and (4) pseudopoly(amino acids) corresponding to a-peptoids [220]. As in tyrosine-derived polycarbonates (discussed in the Polycarbonates section), L-tyrosine is the predominantly employed amino acid in the synthesis of tyrosine-derived polyarylates and polyesters. A combinatorial library of degradable tyrosine-derived polyarylates was synthesized by copolymerizing 14 completely different tyrosine-derived diphenols and eight different aliphatic diacids in all possible mixtures, leading to 112 distinct polymers [221]. Significant differences have been observed in the mechanical properties of the polymers and fibroblast proliferation assays with these supplies. This illustrates that such combinatorial approaches present a library of associated polymers that encompasses a broad vary of properties and permits the systematic examine of material-dependent biological responses so as to select a suitable material for a selected utility. Another amino acid that has obtained interest as a component in artificial polymers for biomedical purposes is L-lysine. Lysine has been investigated as a part in urethane/urea esters, each as a linear block with a free carboxyl group for functionalization [222] and as a three-armed branching point by which the carboxyl group bears an ester with another amino performance. Degradation research of the latter materials pointed to oxidative processes having an important position in the degradation of such a cloth in vivo [223]. In a extra general context, the polymerization of amino acids with side chain functionalities yields polymer chains with pendent useful teams that can be used for additional functionalization. In addition to lysine and tyrosine, different amino acids have been selected for his or her facet chain functionalities [227], together with glutamic acid [228] and 574 L- 33.
16 mg atacand generic
Finally, the obtained scaffolds are lyophilized once more, creating a porous scaffold. In a unique research, ice particulates with completely different sizes had been used as a porogen material to produce scaffolds with completely different pore diameters [24]. For that, collagen was mixed with the ice particulates and freeze-dried, creating spherical pore buildings of various pore sizes and good interconnectivity. Computer-aided manufacturing seems to be a method that enables the production of highly organized scaffolds. It produces extremely porous patterned scaffolds using pure collagen, during which the pore measurement, shape, and spacing may be managed [26]. They combined a cryogenic plotting system, freeze-drying, and electrospinning to produce a secure scaffold with a controlled pore measurement. Collagen in Bone Tissue Engineering Applications Type I collagen is secreted by osteoblasts in the course of the means of ossification; it has necessary roles throughout mineralization. Therefore, enhanced biological integration with the encircling tissue could additionally be foreseen when collagen scaffolds are used in vivo. In vitro, it was shown that collagen/cellulose scaffolds help mobile adhesion and the phenotype upkeep of cultured human osteoblasts [28]. In vivo, collagen scaffolds implanted in crucial bone defects in rat calvaria were biocompatible and extremely osteogenic [29]. In addition, the rate of biodegradation was appropriate with bone neoformation and vessel neoformation. Collagenhydroxyapatite scaffolds induce human adipose derived stem cells osteogenic differentiation in vitro. In a 2-year follow-up report, it was noticed that the strategy favored osteochondral tissue regeneration in treating knees affected by harm of the articular surface in contrast with degenerative lesions. Structurally, this highemolecular weight gum (z500 kDa) incorporates a repeating unit composed of L-rhamnose, D-glucuronic acid, and two D-glucose subunits. The presence of glucuronic acid residues makes this polysaccharide structural similar to native glycosaminoglycans and supports its use for tissue engineering methods. Gellan gum is soluble in water; it types a viscous solution and is insoluble in ethanol, forming precipitates. Its capacity to type precipitates enable its extraction from bacteria inoculates in a medium with glucose, nitrogen, and inorganic salts [32]. When submitted to a excessive temperature, it undergoes a reversible transition conformation from a coil to a double helix upon cooling. The temperature necessary for the transition is decided by the polymer concentration, the degree of acetylation, and the presence of cations [32]. Gellan gum could also be found as high-acyl gellan gum, which is the native acetylated form, and low-acyl gellan gum, which is the commercially obtainable deacetylated type. The difference between these two varieties resides in the presence of glycerate and acetate functionalities in high-acyl gellan gum, which in low-acyl gellan gum are reduced to hydroxyl residues. The discount outcomes from the hot alkaline conditions employed throughout extraction. The degree of acetylation can significantly affect the mechanical properties and gelation properties of gellan gum. In this sense, highacyl gellan gum produces delicate, elastic, thermoreversible gels after cooling from sixty five C, whereas low-acyl gellan gum produces stiff, brittle, thermostable gels after cooling from 40 C. In the first case, gelation occurs owing to ionic cross-linking between the divalent cations and the carboxylate groups, and because of the screening effect, forming stable and powerful bonds. In the second case, gelation occurs solely as a end result of the screening impact, leading to much less stable constructions. Gellan gum matrices have been principally produced by casting; they biodegrade over weeks to months, which is a beautiful characteristic for tissue engineering approaches [33]. However, to understand their degradation pathways and kinetics absolutely, extra studies must be done. If we consider their biological options, such as being processed under gentle situations and never being cytotoxic, and likewise their apparent influence throughout osteogenesis, one can envisage their potential as a biomaterial. Furthermore, due to the hydroxyl groups shaped during deacetylation and the free carboxyl group in the glucuronic acid subunit, they are often modified to improve physicochemical and biological properties.
Marcus, 45 years: Adaptation of such a mechanical drive in culture techniques may significantly promote proplatelet progress and platelet launch, as demonstrated by Thon et al.
Kaelin, 34 years: However, examinations of the internal ears of sharks and rays, which grow indeterminately, indicated an ongoing enhance in the number of hair cells within the inside ear sensory patches of those animals.
Bengerd, 51 years: This poses significant surgical limitations, as a end result of sufferers will need to bear surgery to isolate the donor tissue and then wait a major interval for the fabrication of a construct.
Mortis, 21 years: Microfluidic chip with built-in electrical cell-impedance sensing for monitoring single most cancers cell migration in three-dimensional matrixes.
Xardas, 42 years: The formation of a nanostructured coating layer on the floor of bone implant supplies.
Fraser, 24 years: Although the species distribution of craniofacial an infection has not changed a lot through the years, the antibiotic resistance of those organisms is rising [100].
Nefarius, 61 years: They demonstrated that there was an upregulation of quick myosin heavy chain and a-sarcomeric actinin in contrast with the control gel [37].
Marius, 44 years: Moreover, studies present that the speed of therapeutic of the ligament is asynchronous with the insertion websites due to its anatomical and morphological complexity.
Trompok, 46 years: Coupled with their inherent brittle behavior, this has limited their scientific applicability to noneload bearing or pure compression-loading sites [74,75].
Riordian, 26 years: Finally, in parallel to sacrificial inks, these supplies should be easily detachable to decouple from the finalized printed assemble.
Lares, 22 years: This research suggests that flow-induced shear stresses could additionally be an effective practical tissue-engineering technique for modulating matrix composition and mechanical properties in vitro.
Vatras, 29 years: This article will talk about data concerning tissue engineering totally different areas of the alimentary tract, highlighting profitable strategies in addition to failures and a few obstacles that have but to be overcome in this quickly evolving subject.
Thorald, 55 years: Specifically, osteoclasts can dissolve weak and old bone regions by regionally secreting acidic substances such as protons, whereas osteoblasts can form new bone tissues by secreting proteins similar to collagen.
8 of 10 - Review by J. Kirk
Votes: 26 votes
Total customer reviews: 26
References
- Steg PG, Bonnefoy E, Chabaud S, et al: Impact of time to treatment on mortality after inhospital fibrinolysis or primary angioplasty: data from the CAPTIM randomized clinical trial. Circulation 2003;108:2851-2856.
- Gakis G, Ninkovic M, van Koeveringe GA, et al: Functional detrusor myoplasty for bladder acontractility: long-term results, J Urol 185:593n599, 2011.
- Torvik A, Jorgensen L. Thrombotic and embolic occlusions of the carotid arteries in an autopsy material. Part 2: Cerebral lesions and clinical course. J Neurol Sci 1966;3:410.
- QIU Xing-biao, SHI Hong-yu, LIU Lan, et al. Multiple aorticocameral tunnels associated with bicuspid aortic valve in aged: a case report. Chin Med J. 2009;122:2184-5.
- Tworek JA, Goldblum JR, Weiss SW, et al. Stromal tumors of the abdominal colon: a clinicopathologic study of 20 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1999;23(8):937-945.
- Ron E: Cancer risks from medical radiation, Health Phys 85:47-59, 2003.
- Davis, D.M., Strong, G.H., Drake, W.M. Intubated ureterotomy: Experimental work and clinical results. J Urol 1948;59:851-856.
- Rosenow E, Strimlan CV, Muhm JR, Ferguson RH. Pleuropulmonary manifestations of ankylosing spondylitis. Mayo Clin Proc 1977;52(10):641-9.